| ┌1A. | Plants free-floating aquatics; leaves rosulate, hairy; flowers unisexual, naked; inflorescence with a single female flower and a few male flowers . 105. 📌Pistia
|
| ├1B. | Plants terrestrial or helophyteHelophyte: A bog plant; especially a perennial marsh plant having its overwintering buds under water.
s, climbing hemiepiphyteEpiphyte: A plant that grows harmlessly upon another plant and derives its moisture and nutrients from the air, rain, and sometimes from debris accumulating around it.
s, epiphyteEpiphyte: A plant that grows harmlessly upon another plant and derives its moisture and nutrients from the air, rain, and sometimes from debris accumulating around it.
s or lithophyteLithophyte: A plant that grows on bare rock or stone.
s or other, but never floating
|
| │ | ┌2A. | Leaves not differentiated into petiolePetiole: Leaf stem. and blade, primary venationVenation: The arrangement of veins in the leaf.
and blade, primary venationVenation: The arrangement of veins in the leaf. strictly parallelParallel: Parallel Venation.
strictly parallelParallel: Parallel Venation.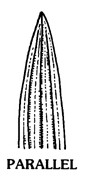 ; inflorescence borne on a culm-like axis
; inflorescence borne on a culm-like axis
|
| │ | │ | ┌3A. | Leaves ensiformEnsiform: Shaped like a sword blade; long and narrow with sharp edges and a pointed tip.
, unifacialUnifacial: In unifacial leaves, the upper sides are undeveloped and the whole leaf surface develops from the morphological lower side.
; spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe. solitary, pseudolateral and overtopped by a single, erect, leaf-like spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
solitary, pseudolateral and overtopped by a single, erect, leaf-like spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. ; flowers 3-merous, tepalTepal: A segment of the outer whorl in a flower that has no differentiation between petals and sepals.
s .6. 📌Acorus (Acoraceae)
; flowers 3-merous, tepalTepal: A segment of the outer whorl in a flower that has no differentiation between petals and sepals.
s .6. 📌Acorus (Acoraceae)
|
| │ | │ | └3B. | Leaves dorsiventrally flattened, bifacial; flowering shoot with long culm-like axis, bearing numerous spadices distally, these borne in axillary clusters subtendSubtend: (of a bract) extend under (a flower) so as to support or enfold it.
ed by elongate bracts; flowers 2-merous, tepalTepal: A segment of the outer whorl in a flower that has no differentiation between petals and sepals.
s 4 .1. 📌Gymnostachys
|
| │ | ├2B. | Leaves with distinct petiolePetiole: Leaf stem. and expanded blade, primary venationVenation: The arrangement of veins in the leaf.
and expanded blade, primary venationVenation: The arrangement of veins in the leaf. never strictly parallelParallel: Parallel Venation.
never strictly parallelParallel: Parallel Venation.
|
| │ | │ | ┌4A. | Flowers with obvious perigonePerigone: The outer part of a flower, consisting of the calyx (sepals) and corolla (petals).
of free or fused tepalTepal: A segment of the outer whorl in a flower that has no differentiation between petals and sepals.
s (except Pycnospatha which lacks perigonePerigone: The outer part of a flower, consisting of the calyx (sepals) and corolla (petals).
, but has dracontioidDracontioid:  leaf, tuberous stem and boat-shaped, fornicateFornicate: Arched or bending over.
spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
leaf, tuberous stem and boat-shaped, fornicateFornicate: Arched or bending over.
spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. - see lead 22)
- see lead 22)
|
| │ | │ | │ | ┌5A. | Flowers bisexual, spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe. uniform in appearance with flowers of only one type
uniform in appearance with flowers of only one type
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌6A. | Higher order leaf venationVenation: The arrangement of veins in the leaf. parallel-pinnateParallel-pinnate: Parallel-Pinnate Venation.
parallel-pinnateParallel-pinnate: Parallel-Pinnate Venation. ; tissues with abundant trichosclereidTrichosclereid: A hard, needle-like branched cell.
s
; tissues with abundant trichosclereidTrichosclereid: A hard, needle-like branched cell.
s
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌7A. | SpatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. persistentPersistent: Remaining attached to the plant beyond the usual time of falling.
; tepalTepal: A segment of the outer whorl in a flower that has no differentiation between petals and sepals.
s free or connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
; ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals.
persistentPersistent: Remaining attached to the plant beyond the usual time of falling.
; tepalTepal: A segment of the outer whorl in a flower that has no differentiation between petals and sepals.
s free or connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
; ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals. 2-4-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
2-4-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary. ; ovuleOvule: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells
; ovuleOvule: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells s 2-8 per loculeLocule: A small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
s 2-8 per loculeLocule: A small cavity or compartment within an ovary. , placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta.
, placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta. axile .9. 📌Spathiphyllum
axile .9. 📌Spathiphyllum
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | └7B. | SpatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. deliquescentDeliquescent: Having a tendency to become liquid.
; tepalTepal: A segment of the outer whorl in a flower that has no differentiation between petals and sepals.
s connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
; ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals.
deliquescentDeliquescent: Having a tendency to become liquid.
; tepalTepal: A segment of the outer whorl in a flower that has no differentiation between petals and sepals.
s connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
; ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals. 1-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
1-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary. ; ovuleOvule: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells
; ovuleOvule: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells s several, placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta.
s several, placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta. basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
.10. 📌Holochlamys
basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
.10. 📌Holochlamys
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | ├6B. | Higher order leaf venationVenation: The arrangement of veins in the leaf. clearly reticulateReticulate: Reticulate Venation.
clearly reticulateReticulate: Reticulate Venation. d; tissues without trichosclereidTrichosclereid: A hard, needle-like branched cell.
s or trichosclereidTrichosclereid: A hard, needle-like branched cell.
s very few
d; tissues without trichosclereidTrichosclereid: A hard, needle-like branched cell.
s or trichosclereidTrichosclereid: A hard, needle-like branched cell.
s very few
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌8A. | Stem aerial, not tuberous or rhizomatous, never aculeateAculeate: Sharply pointed; prickly.
; plant usually a climbing hemiepiphyteEpiphyte: A plant that grows harmlessly upon another plant and derives its moisture and nutrients from the air, rain, and sometimes from debris accumulating around it.
or epiphyteEpiphyte: A plant that grows harmlessly upon another plant and derives its moisture and nutrients from the air, rain, and sometimes from debris accumulating around it.
, less often lithophyteLithophyte: A plant that grows on bare rock or stone.
or terrestrial, only very rarely helophyticHelophytic: A bog plant; especially a perennial marsh plant having its overwintering buds under water.
(some spp. of Anthurium)
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌9A. | Neotropical plants; seeds with copious endospermEndosperm: A tissue produced inside the seeds of most of the flowering plants following fertilization. It surrounds the embryo and provides nutrition in the form of starch, though it can also contain oils and protein.
; pollen usually forateForate: With aperatures or openings.
, never monosulcateSulcate: Furrowed; grooved.
.8. 📌Anthurium
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ├9B. | Palaeotropical plants; seeds without endospermEndosperm: A tissue produced inside the seeds of most of the flowering plants following fertilization. It surrounds the embryo and provides nutrition in the form of starch, though it can also contain oils and protein.
; pollen monosulcateSulcate: Furrowed; grooved.
or inaperturateInaperturate: Without an opening.
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌10A. | StigmaStigma: The receptive tip of a carpel, or of several fused carpels, in the gynoecium of a flower. transversely oblongOblong:
transversely oblongOblong:  ; stamenStamen: The pollen-producing reproductive organ of a flower.
; stamenStamen: The pollen-producing reproductive organ of a flower. s always 4 per flower; pollen inaperturateInaperturate: Without an opening.
; perigonePerigone: The outer part of a flower, consisting of the calyx (sepals) and corolla (petals).
consisting of a single cup-like structure .11. 📌Anadendrum
s always 4 per flower; pollen inaperturateInaperturate: Without an opening.
; perigonePerigone: The outer part of a flower, consisting of the calyx (sepals) and corolla (petals).
consisting of a single cup-like structure .11. 📌Anadendrum
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ├10B. | StigmaStigma: The receptive tip of a carpel, or of several fused carpels, in the gynoecium of a flower. hemispheric to discoid; stamenStamen: The pollen-producing reproductive organ of a flower.
hemispheric to discoid; stamenStamen: The pollen-producing reproductive organ of a flower. s usually 6 per flower; pollen monosulcateSulcate: Furrowed; grooved.
; perigonePerigone: The outer part of a flower, consisting of the calyx (sepals) and corolla (petals).
usually consisting of free tepalTepal: A segment of the outer whorl in a flower that has no differentiation between petals and sepals.
s or when connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
and cup-like the flowers are borne on short pedicels
s usually 6 per flower; pollen monosulcateSulcate: Furrowed; grooved.
; perigonePerigone: The outer part of a flower, consisting of the calyx (sepals) and corolla (petals).
usually consisting of free tepalTepal: A segment of the outer whorl in a flower that has no differentiation between petals and sepals.
s or when connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
and cup-like the flowers are borne on short pedicels
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌11A. | OvaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals. 3-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
3-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary. ; loculeLocule: A small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
; loculeLocule: A small cavity or compartment within an ovary. s 1-ovulateOvulate: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells
s 1-ovulateOvulate: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells ; flowering shoot with inflorescences always axillary
; flowering shoot with inflorescences always axillary
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌12A. | Flowers sessileSessile: Attached directly by its base without a stalk or peduncle.
; tepalTepal: A segment of the outer whorl in a flower that has no differentiation between petals and sepals.
s free, very rarely basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
ly united .5. 📌Pothos
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | └12B. | Flowers pedicellatePedicellate: A flower having a stalk is called pedunculate or pedicellate.
; tepalTepal: A segment of the outer whorl in a flower that has no differentiation between petals and sepals.
s connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
.6. 📌Pedicellarum
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | └11B. | OvaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals. 1-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
1-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary. ; flowering shoots terminating in a branching system of spadices .7. 📌Pothoidium
; flowering shoots terminating in a branching system of spadices .7. 📌Pothoidium
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ├8B. | Stem typically subterranean, tuberous or rhizomatous, sometimes aerial and creeping or scrambling but then aculeateAculeate: Sharply pointed; prickly.
; plant frequently a helophyteHelophyte: A bog plant; especially a perennial marsh plant having its overwintering buds under water.
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌13A. | Plants of temperate regions (N. America, NE. Asia); leaf blade always entire, ovateOvate:  to ellipticElliptic:
to ellipticElliptic: 
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌14A. | OvaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals. 2-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
2-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary. ; ovuleOvule: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells
; ovuleOvule: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells s 2 per loculeLocule: A small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
s 2 per loculeLocule: A small cavity or compartment within an ovary. , placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta.
, placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta. axile .3. 📌Lysichiton
axile .3. 📌Lysichiton
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ├14B. | OvaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals. 1-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
1-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary. ; ovuleOvule: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells
; ovuleOvule: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells 1, placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta.
1, placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta. apicalApical: Of, relating to, or denoting an apex.
or basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
apicalApical: Of, relating to, or denoting an apex.
or basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌15A. | PlacentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta. basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
; spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
; spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. inconspicuous; spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe.
inconspicuous; spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe. cylindric, stipeStipe: A stalk or stem.
very long .2. 📌Orontium
cylindric, stipeStipe: A stalk or stem.
very long .2. 📌Orontium
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | └15B. | PlacentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta. apicalApical: Of, relating to, or denoting an apex.
; spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
apicalApical: Of, relating to, or denoting an apex.
; spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. thick, ventricoseVentricose: Distended, inflated. Having a protruding belly.
, enclosing spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe.
thick, ventricoseVentricose: Distended, inflated. Having a protruding belly.
, enclosing spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe. ; spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe.
; spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe. subgloboseSubglobose: Imperfectly globose ( globe-shaped ).
, stipeStipe: A stalk or stem.
short .4. 📌Symplocarpus
subgloboseSubglobose: Imperfectly globose ( globe-shaped ).
, stipeStipe: A stalk or stem.
short .4. 📌Symplocarpus
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ├13B. | Plants of tropical and subtropical regions; leaf blade sagittateSagittate:  , pinnatifidPinnatifid:
, pinnatifidPinnatifid:  , pinnatisectPinnatisect: Having lobes with incisions that extend almost, or up to midrib.
, pinnatisectPinnatisect: Having lobes with incisions that extend almost, or up to midrib. or dracontioidDracontioid:
or dracontioidDracontioid: 
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌16A. | Leaf deeply sagittateSagittate:  , anteriorAnterior:
, anteriorAnterior:  division not pinnatifidPinnatifid:
division not pinnatifidPinnatifid:  or pinnatisectPinnatisect: Having lobes with incisions that extend almost, or up to midrib.
or pinnatisectPinnatisect: Having lobes with incisions that extend almost, or up to midrib.
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌17A. | OvaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals. many- to 2-ovulateOvulate: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells
many- to 2-ovulateOvulate: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells , rarely 1-ovulateOvulate: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells
, rarely 1-ovulateOvulate: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells ; seeds with endospermEndosperm: A tissue produced inside the seeds of most of the flowering plants following fertilization. It surrounds the embryo and provides nutrition in the form of starch, though it can also contain oils and protein.
; seeds with endospermEndosperm: A tissue produced inside the seeds of most of the flowering plants following fertilization. It surrounds the embryo and provides nutrition in the form of starch, though it can also contain oils and protein.
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌18A. | Plants without stolons; petiolePetiole: Leaf stem. spines dispersed; stamenStamen: The pollen-producing reproductive organ of a flower.
spines dispersed; stamenStamen: The pollen-producing reproductive organ of a flower. filaments free; tropical Asia to Oceania .26. 📌Cyrtosperma
filaments free; tropical Asia to Oceania .26. 📌Cyrtosperma
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | └18B. | Plants with long stolons; petiolePetiole: Leaf stem. spines in ridges; stamenStamen: The pollen-producing reproductive organ of a flower.
spines in ridges; stamenStamen: The pollen-producing reproductive organ of a flower. filaments free or connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
; tropical West Africa .27. 📌Lasimorpha
filaments free or connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
; tropical West Africa .27. 📌Lasimorpha
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ├17B. | OvaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals. 1-ovulateOvulate: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells
1-ovulateOvulate: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells , rarely 2-ovulateOvulate: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells
, rarely 2-ovulateOvulate: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells ; seeds without endospermEndosperm: A tissue produced inside the seeds of most of the flowering plants following fertilization. It surrounds the embryo and provides nutrition in the form of starch, though it can also contain oils and protein.
or rarely with a little endospermEndosperm: A tissue produced inside the seeds of most of the flowering plants following fertilization. It surrounds the embryo and provides nutrition in the form of starch, though it can also contain oils and protein.
; seeds without endospermEndosperm: A tissue produced inside the seeds of most of the flowering plants following fertilization. It surrounds the embryo and provides nutrition in the form of starch, though it can also contain oils and protein.
or rarely with a little endospermEndosperm: A tissue produced inside the seeds of most of the flowering plants following fertilization. It surrounds the embryo and provides nutrition in the form of starch, though it can also contain oils and protein.
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌19A. | PetiolePetiole: Leaf stem. aculeateAculeate: Sharply pointed; prickly.
, with obvious spines; Malay Archipelago .28. 📌Podolasia
aculeateAculeate: Sharply pointed; prickly.
, with obvious spines; Malay Archipelago .28. 📌Podolasia
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ├19B. | PetiolePetiole: Leaf stem. smooth to scabrid-verrucoseVerrucose: Covered with warts or wartlike projections.
, never aculeateAculeate: Sharply pointed; prickly.
; tropical America
smooth to scabrid-verrucoseVerrucose: Covered with warts or wartlike projections.
, never aculeateAculeate: Sharply pointed; prickly.
; tropical America
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌20A. | Leaf blade never fenestrateFenestrate: Having large openings or windows.
; spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. lanceolateLanceolate:
lanceolateLanceolate:  , very long-acuminateAcuminate: Tapering to a point.
and usually spirally twisted; ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals.
, very long-acuminateAcuminate: Tapering to a point.
and usually spirally twisted; ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals. loculeLocule: A small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
loculeLocule: A small cavity or compartment within an ovary. s with (1-)2 to several ovuleOvule: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells
s with (1-)2 to several ovuleOvule: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells s; neotropics .30. 📌Urospatha
s; neotropics .30. 📌Urospatha
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | └20B. | Leaf blade often perforateForate: With aperatures or openings.
d with a few perforations of irregular size between primary lateral veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.  s; spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
s; spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. fornicateFornicate: Arched or bending over.
; endemic to Brazil (coastal Bahia and Espirito Santo) .22. 📌Dracontioides
fornicateFornicate: Arched or bending over.
; endemic to Brazil (coastal Bahia and Espirito Santo) .22. 📌Dracontioides
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ├16B. | Leaf blade pinnatifidPinnatifid:  , pinnatisectPinnatisect: Having lobes with incisions that extend almost, or up to midrib.
, pinnatisectPinnatisect: Having lobes with incisions that extend almost, or up to midrib. , dracontioidDracontioid:
, dracontioidDracontioid:  or sometimes ± pedatifid; anteriorAnterior:
or sometimes ± pedatifid; anteriorAnterior:  division always pinnatePinnate: Pinnate Venation.
division always pinnatePinnate: Pinnate Venation.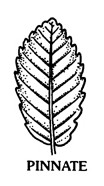 ly divided, either pinnatifidPinnatifid:
ly divided, either pinnatifidPinnatifid:  , pinnatisectPinnatisect: Having lobes with incisions that extend almost, or up to midrib.
, pinnatisectPinnatisect: Having lobes with incisions that extend almost, or up to midrib. or yet more highly divided
or yet more highly divided
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌21A. | Stem aculeateAculeate: Sharply pointed; prickly.
, aerial and scrambling to prostrate, internodes distinct, green.29. 📌Lasia
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ├21B. | Stem not aculeateAculeate: Sharply pointed; prickly.
, subterranean, internodes very abbreviated, not green
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌22A. | Leaf blade dracontioidDracontioid:  , anteriorAnterior:
, anteriorAnterior:  division bipinnatifidPinnatifid:
division bipinnatifidPinnatifid:  or yet more highly divided; stem a depressed-globose tuber; spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
or yet more highly divided; stem a depressed-globose tuber; spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. fornicateFornicate: Arched or bending over.
fornicateFornicate: Arched or bending over.
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌23A. | Tropical America; flowers with perigonePerigone: The outer part of a flower, consisting of the calyx (sepals) and corolla (petals).
of 4-8 free tepalTepal: A segment of the outer whorl in a flower that has no differentiation between petals and sepals.
s; berries smooth, red .21. 📌Dracontium
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | └23B. | Tropical southeast Asia; flowers without perigonePerigone: The outer part of a flower, consisting of the calyx (sepals) and corolla (petals).
; berries aculeateAculeate: Sharply pointed; prickly.
, dark green .24. 📌Pycnospatha
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ├22B. | Leaf blade pinnatifidPinnatifid:  , pinnatisectPinnatisect: Having lobes with incisions that extend almost, or up to midrib.
, pinnatisectPinnatisect: Having lobes with incisions that extend almost, or up to midrib. , or sometimes ± pedatifid, anteriorAnterior:
, or sometimes ± pedatifid, anteriorAnterior:  division pinnatifidPinnatifid:
division pinnatifidPinnatifid:  to pinnatisectPinnatisect: Having lobes with incisions that extend almost, or up to midrib.
to pinnatisectPinnatisect: Having lobes with incisions that extend almost, or up to midrib. ; stem a vertical or horizontal rhizome; spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
; stem a vertical or horizontal rhizome; spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. erect, not fornicateFornicate: Arched or bending over.
, blade often spirally twisted apicalApical: Of, relating to, or denoting an apex.
ly
erect, not fornicateFornicate: Arched or bending over.
, blade often spirally twisted apicalApical: Of, relating to, or denoting an apex.
ly
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌24A. | Tropical America; testa thick, verrucoseVerrucose: Covered with warts or wartlike projections.
; embryo curved .23. 📌Anaphyllopsis
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | └24B. | Southern India; testa membranous, smooth; embryo straight .25. 📌Anaphyllum
|
| │ | │ | │ | ├5B. | Flowers unisexual, spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe. clearly divided into basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
female zone and apicalApical: Of, relating to, or denoting an apex.
male zone; tropical Africa
clearly divided into basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
female zone and apicalApical: Of, relating to, or denoting an apex.
male zone; tropical Africa
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌25A. | Leaf pinnatisectPinnatisect: Having lobes with incisions that extend almost, or up to midrib. to tri- or quadripinnatifidPinnatifid:
to tri- or quadripinnatifidPinnatifid:  ; tepalTepal: A segment of the outer whorl in a flower that has no differentiation between petals and sepals.
s free; spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
; tepalTepal: A segment of the outer whorl in a flower that has no differentiation between petals and sepals.
s free; spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. margins free
margins free
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌26A. | Leaf blade pinnatisectPinnatisect: Having lobes with incisions that extend almost, or up to midrib. ; stamenStamen: The pollen-producing reproductive organ of a flower.
; stamenStamen: The pollen-producing reproductive organ of a flower. s free .32. 📌Zamioculcas
s free .32. 📌Zamioculcas
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | └26B. | Leaf blade bipinnatifidPinnatifid:  to quadripinnatifidPinnatifid:
to quadripinnatifidPinnatifid:  , at least in lowest pinnaPinna: A primary division of a pinnate leaf.
e; stamenStamen: The pollen-producing reproductive organ of a flower.
, at least in lowest pinnaPinna: A primary division of a pinnate leaf.
e; stamenStamen: The pollen-producing reproductive organ of a flower. filaments connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
.33. 📌Gonatopus
filaments connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
.33. 📌Gonatopus
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | └25B. | Leaf entire, linearLinear:  to cordateCordate:
to cordateCordate:  , sagittateSagittate:
, sagittateSagittate:  or hastateHastate:
or hastateHastate:  ; tepalTepal: A segment of the outer whorl in a flower that has no differentiation between petals and sepals.
s connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
into cup; spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
; tepalTepal: A segment of the outer whorl in a flower that has no differentiation between petals and sepals.
s connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
into cup; spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. margins connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
ly .34. 📌Stylochaeton
margins connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
ly .34. 📌Stylochaeton
|
| │ | │ | ├4B. | Flowers without perigon of free or fused tepalTepal: A segment of the outer whorl in a flower that has no differentiation between petals and sepals.
s
|
| │ | │ | │ | ┌27A. | Flowers bisexual; spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe. uniform in appearance with flowers of only one type (sometimes with sterile flowers at spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe.
uniform in appearance with flowers of only one type (sometimes with sterile flowers at spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe. base)
base)
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌28A. | HelophyteHelophyte: A bog plant; especially a perennial marsh plant having its overwintering buds under water.
s from temperate regions of northern hemisphere; petiolePetiole: Leaf stem. sheath with long apicalApical: Of, relating to, or denoting an apex.
liguleLigule: A narrow strap-shaped part of a plant, especially a membranous scale on the inner side of the leaf sheath at its junction with the blade.
.31. 📌Calla
sheath with long apicalApical: Of, relating to, or denoting an apex.
liguleLigule: A narrow strap-shaped part of a plant, especially a membranous scale on the inner side of the leaf sheath at its junction with the blade.
.31. 📌Calla
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | ├28B. | Climbing hemiepiphyteEpiphyte: A plant that grows harmlessly upon another plant and derives its moisture and nutrients from the air, rain, and sometimes from debris accumulating around it.
s or sometimes epiphyteEpiphyte: A plant that grows harmlessly upon another plant and derives its moisture and nutrients from the air, rain, and sometimes from debris accumulating around it.
s or very rarely rheophyteRheophyte: An aquatic plant that lives in fast moving water currents.
s (few Rhaphidophora) from tropical regions; petiolePetiole: Leaf stem. sheath non-ligulateLigulate: Having a narrow strap-shaped part, especially a membranous scale on the inner side of the leaf sheath at its junction with the blade.
or liguleLigule: A narrow strap-shaped part of a plant, especially a membranous scale on the inner side of the leaf sheath at its junction with the blade.
only short
sheath non-ligulateLigulate: Having a narrow strap-shaped part, especially a membranous scale on the inner side of the leaf sheath at its junction with the blade.
or liguleLigule: A narrow strap-shaped part of a plant, especially a membranous scale on the inner side of the leaf sheath at its junction with the blade.
only short
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌29A. | PetiolePetiole: Leaf stem. usually very short with non-annular insertion; trichosclereidTrichosclereid: A hard, needle-like branched cell.
s not present in tissues, leaf never perforateForate: With aperatures or openings.
d or lobed; primary lateral veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.
usually very short with non-annular insertion; trichosclereidTrichosclereid: A hard, needle-like branched cell.
s not present in tissues, leaf never perforateForate: With aperatures or openings.
d or lobed; primary lateral veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.  s forming distinct submarginal veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.
s forming distinct submarginal veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.  .8. 📌Heteropsis
.8. 📌Heteropsis
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ├29B. | PetiolePetiole: Leaf stem. well-developed with annular insertion and usually conspicuous sheath; trichosclereidTrichosclereid: A hard, needle-like branched cell.
s present in tissues, or if absent (or nearly so) then leaf with conspicuously reticulateReticulate: Reticulate Venation.
well-developed with annular insertion and usually conspicuous sheath; trichosclereidTrichosclereid: A hard, needle-like branched cell.
s present in tissues, or if absent (or nearly so) then leaf with conspicuously reticulateReticulate: Reticulate Venation. higher order venationVenation: The arrangement of veins in the leaf.
higher order venationVenation: The arrangement of veins in the leaf. and often perforateForate: With aperatures or openings.
d or lobed (Amydrium); primary lateral veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.
and often perforateForate: With aperatures or openings.
d or lobed (Amydrium); primary lateral veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.  s usually not forming distinct submarginal veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.
s usually not forming distinct submarginal veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins. 
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌30A. | TrichosclereidTrichosclereid: A hard, needle-like branched cell.
s rare or nearly absent; higher order leaf venationVenation: The arrangement of veins in the leaf. completely reticulateReticulate: Reticulate Venation.
completely reticulateReticulate: Reticulate Venation. ; ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals.
; ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals. 1-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
1-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary. , placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta.
, placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta. 1, intrusive-parietal, ovuleOvule: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells
1, intrusive-parietal, ovuleOvule: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells s 2 .13. 📌Amydrium
s 2 .13. 📌Amydrium
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ├30B. | TrichosclereidTrichosclereid: A hard, needle-like branched cell.
s abundant; higher order leaf venationVenation: The arrangement of veins in the leaf. parallelParallel: Parallel Venation.
parallelParallel: Parallel Venation. to primary lateral veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.
to primary lateral veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.  s, or only finest venationVenation: The arrangement of veins in the leaf.
s, or only finest venationVenation: The arrangement of veins in the leaf. reticulateReticulate: Reticulate Venation.
reticulateReticulate: Reticulate Venation.
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌31A. | OvaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals. 1-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
1-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary. or incompletely 2-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
or incompletely 2-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌32A. | OvuleOvule: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells s anatropous, more than one
s anatropous, more than one
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌33A. | OvuleOvule: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells s numerous, superposed on 2 (rarely 3) parietal placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta.
s numerous, superposed on 2 (rarely 3) parietal placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta. s; seeds fusiform, straight, 1.3-3.2 mm long, 0.6-1.0 mm wide.14. 📌Rhaphidophora
s; seeds fusiform, straight, 1.3-3.2 mm long, 0.6-1.0 mm wide.14. 📌Rhaphidophora
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | └33B. | OvuleOvule: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells s 2-4 (-6) at base of a single intrusive placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta.
s 2-4 (-6) at base of a single intrusive placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta. ; seeds curved, 3-7 mm long, 1.5-4.0 mm wide .15. 📌Epipremnum
; seeds curved, 3-7 mm long, 1.5-4.0 mm wide .15. 📌Epipremnum
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ├32B. | OvuleOvule: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells s amphitropous to anatropous, solitary, basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
s amphitropous to anatropous, solitary, basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌34A. | Adult leaf blade entire; palaeotropics .16. 📌Scindapsus
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | └34B. | Adult leaf blade pinnatifidPinnatifid:  ; neotropics (Amazonia) 18. 📌Alloschemone
; neotropics (Amazonia) 18. 📌Alloschemone
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ├31B. | OvaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals. 2-5 locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
2-5 locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌35A. | Seeds fusiform, claviform or lenticular, less than 3 mm long, endospermEndosperm: A tissue produced inside the seeds of most of the flowering plants following fertilization. It surrounds the embryo and provides nutrition in the form of starch, though it can also contain oils and protein.
present; ovuleOvule: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells s (2-)3-many per loculeLocule: A small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
s (2-)3-many per loculeLocule: A small cavity or compartment within an ovary. ; leaf blade entire
; leaf blade entire
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌36A. | PlacentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta. basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
; seeds fusiform to claviform; leaf blades thickly coriaceousCoriaceous: Resembling or having the texture of leather.
.20. 📌Stenospermation
basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
; seeds fusiform to claviform; leaf blades thickly coriaceousCoriaceous: Resembling or having the texture of leather.
.20. 📌Stenospermation
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | └36B. | PlacentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta. axile; seeds lenticular and flattened, strongly curved; leaf blades mostly membranous .19. 📌Rhodospatha
axile; seeds lenticular and flattened, strongly curved; leaf blades mostly membranous .19. 📌Rhodospatha
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | └35B. | Seeds globose to oblongOblong:  , 6-22 mm long, the raphe S-shaped; endospermEndosperm: A tissue produced inside the seeds of most of the flowering plants following fertilization. It surrounds the embryo and provides nutrition in the form of starch, though it can also contain oils and protein.
absent; ovuleOvule: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells
, 6-22 mm long, the raphe S-shaped; endospermEndosperm: A tissue produced inside the seeds of most of the flowering plants following fertilization. It surrounds the embryo and provides nutrition in the form of starch, though it can also contain oils and protein.
absent; ovuleOvule: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells s 2 per loculeLocule: A small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
s 2 per loculeLocule: A small cavity or compartment within an ovary. ; leaf blade variously shaped, often perforateForate: With aperatures or openings.
d or pinnatifidPinnatifid:
; leaf blade variously shaped, often perforateForate: With aperatures or openings.
d or pinnatifidPinnatifid:  or both .17. 📌Monstera
or both .17. 📌Monstera
|
| │ | │ | │ | ├27B. | Flowers unisexual; spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe. clearly divided into basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
female zone and apicalApical: Of, relating to, or denoting an apex.
or intermediate male zone, flowers very rarely in longitudinal rows (Spathicarpa)
clearly divided into basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
female zone and apicalApical: Of, relating to, or denoting an apex.
or intermediate male zone, flowers very rarely in longitudinal rows (Spathicarpa)
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌37A. | SpadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe. fused laterally on both sides to spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
fused laterally on both sides to spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. and entirely enclosed by it, forming a septumSeptum: A partition that separates the locules of a fruit, anther, or sporangium.
dividing the spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
and entirely enclosed by it, forming a septumSeptum: A partition that separates the locules of a fruit, anther, or sporangium.
dividing the spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. into two chambers, with a single gynoecium on one side and the male flowers arranged in 2 rows on the other; very small, seasonally dormant plants endemic to western Mediterranean .87. 📌Ambrosina
into two chambers, with a single gynoecium on one side and the male flowers arranged in 2 rows on the other; very small, seasonally dormant plants endemic to western Mediterranean .87. 📌Ambrosina
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | ├37B. | SpadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe. free or fused to spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
free or fused to spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. in various degrees but never fused laterally on both sides to spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
in various degrees but never fused laterally on both sides to spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. to form two internal chambers with a single gynoecium on one side and the male flowers on the other
to form two internal chambers with a single gynoecium on one side and the male flowers on the other
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌38A. | StamenStamen: The pollen-producing reproductive organ of a flower. s of each male flower free or only the filaments connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
s of each male flower free or only the filaments connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌39A. | SpadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe. never entirely enclosed by spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
never entirely enclosed by spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. in a basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
"kettle" formed of connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
in a basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
"kettle" formed of connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. margins (if spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
margins (if spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. margins basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
ly connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
then plant never aquatic)
margins basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
ly connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
then plant never aquatic)
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌40A. | Higher order leaf venationVenation: The arrangement of veins in the leaf. parallel-pinnateParallel-pinnate: Parallel-Pinnate Venation.
parallel-pinnateParallel-pinnate: Parallel-Pinnate Venation.
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌41A. | Upper part of spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. persisting as long as lower part; petiolePetiole: Leaf stem.
persisting as long as lower part; petiolePetiole: Leaf stem. sheath lacking liguleLigule: A narrow strap-shaped part of a plant, especially a membranous scale on the inner side of the leaf sheath at its junction with the blade.
; ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals.
sheath lacking liguleLigule: A narrow strap-shaped part of a plant, especially a membranous scale on the inner side of the leaf sheath at its junction with the blade.
; ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals. 1-many locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
1-many locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary. ; thecaeThecae: One of the lobes of an anther in which pollen is produced.
dehiscing by subapicalApical: Of, relating to, or denoting an apex.
pores or longitudinal slits; connective usually conspicuously thickened
; thecaeThecae: One of the lobes of an anther in which pollen is produced.
dehiscing by subapicalApical: Of, relating to, or denoting an apex.
pores or longitudinal slits; connective usually conspicuously thickened
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌42A. | SpatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. variously shaped, never campanulate; plants tropical American or tropical Asian; pedunclePeduncle: Flower stem.
variously shaped, never campanulate; plants tropical American or tropical Asian; pedunclePeduncle: Flower stem. usually short, if long then female flowers in single whorl (Aglaodorum)
usually short, if long then female flowers in single whorl (Aglaodorum)
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌43A. | Plant always terrestrial, rarely aquatic, never climbing or epiphyticEpiphytic: A plant that grows harmlessly upon another plant and derives its moisture and nutrients from the air, rain, and sometimes from debris accumulating around it.
; inflorescences not secreting resin at anthesisAnthesis: The period during which pollen is presented and/or the stigma is receptive.
; endotheciumEndothecium: The lining of the cavity of an anther.
with cell wall thickenings; ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals. 1 locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
1 locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary. or incompletely 2-5 locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
or incompletely 2-5 locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary. ; most tropical Asian (except Homalomena sect. Curmeria)
; most tropical Asian (except Homalomena sect. Curmeria)
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌44A. | Seed without endospermEndosperm: A tissue produced inside the seeds of most of the flowering plants following fertilization. It surrounds the embryo and provides nutrition in the form of starch, though it can also contain oils and protein.
, embryo large; ovuleOvule: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells 1, placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta.
1, placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta. basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
or parietal
basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
or parietal
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌45A. | Inflorescence with short pedunclePeduncle: Flower stem. ; female flowers in spirals; stem erect to repent; placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta.
; female flowers in spirals; stem erect to repent; placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta. basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
; forest plants.72. 📌Aglaonema
basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
; forest plants.72. 📌Aglaonema
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | └45B. | Inflorescence with long pedunclePeduncle: Flower stem. ; female flowers in a single whorl; stem repent; placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta.
; female flowers in a single whorl; stem repent; placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta. parietal; on tidal mudflats.73. 📌Aglaodorum
parietal; on tidal mudflats.73. 📌Aglaodorum
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ├44B. | Seed with copious endospermEndosperm: A tissue produced inside the seeds of most of the flowering plants following fertilization. It surrounds the embryo and provides nutrition in the form of starch, though it can also contain oils and protein.
, embryo relatively small; ovuleOvule: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells s several to many, placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta.
s several to many, placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta. basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
, parietal or axile
basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
, parietal or axile
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌46A. | Male flower consisting of solitary stamenStamen: The pollen-producing reproductive organ of a flower. overtopped by flask-shaped pistillodePistillode: A sterile vestigial pistil remaining in a staminate flower.
; ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals.
overtopped by flask-shaped pistillodePistillode: A sterile vestigial pistil remaining in a staminate flower.
; ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals. 1-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
1-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary. , placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta.
, placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta. basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
.46. 📌Furtadoa
basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
.46. 📌Furtadoa
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | └46B. | Male flower consisting of 2-6 stamenStamen: The pollen-producing reproductive organ of a flower. s, pistillodePistillode: A sterile vestigial pistil remaining in a staminate flower.
s absent; ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals.
s, pistillodePistillode: A sterile vestigial pistil remaining in a staminate flower.
s absent; ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals. incompletely 2-5 locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
incompletely 2-5 locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary. , placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta.
, placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta. s parietal and axile .47. 📌Homalomena
s parietal and axile .47. 📌Homalomena
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | └43B. | Plant usually climbing or epiphyticEpiphytic: A plant that grows harmlessly upon another plant and derives its moisture and nutrients from the air, rain, and sometimes from debris accumulating around it.
; inflorescences secreting resin from spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. or spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe.
or spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe. at anthesisAnthesis: The period during which pollen is presented and/or the stigma is receptive.
; endotheciumEndothecium: The lining of the cavity of an anther.
nearly always lacking cell wall thickenings; ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals.
at anthesisAnthesis: The period during which pollen is presented and/or the stigma is receptive.
; endotheciumEndothecium: The lining of the cavity of an anther.
nearly always lacking cell wall thickenings; ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals. completely 2-many locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
completely 2-many locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary. , placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta.
, placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta. axile to basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
; tropical America .45. 📌Philodendron
axile to basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
; tropical America .45. 📌Philodendron
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | └42B. | SpatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. obconic to campanulate; plants from Southern Africa (naturalized in America and Asia); pedunclePeduncle: Flower stem.
obconic to campanulate; plants from Southern Africa (naturalized in America and Asia); pedunclePeduncle: Flower stem. long, sometimes longer than leaves .77. 📌Zantedeschia
long, sometimes longer than leaves .77. 📌Zantedeschia
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ├41B. | Upper part of spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. marcescentMarcescent: Withering but remaining attached to the stem.
or caducousCaducous: Easily detached and shed at an early stage.
at anthesisAnthesis: The period during which pollen is presented and/or the stigma is receptive.
, lower part long-persistentPersistent: Remaining attached to the plant beyond the usual time of falling.
; petiolePetiole: Leaf stem.
marcescentMarcescent: Withering but remaining attached to the stem.
or caducousCaducous: Easily detached and shed at an early stage.
at anthesisAnthesis: The period during which pollen is presented and/or the stigma is receptive.
, lower part long-persistentPersistent: Remaining attached to the plant beyond the usual time of falling.
; petiolePetiole: Leaf stem. sheath with long, marcescentMarcescent: Withering but remaining attached to the stem.
liguleLigule: A narrow strap-shaped part of a plant, especially a membranous scale on the inner side of the leaf sheath at its junction with the blade.
(except most Schismatoglottis spp.); ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals.
sheath with long, marcescentMarcescent: Withering but remaining attached to the stem.
liguleLigule: A narrow strap-shaped part of a plant, especially a membranous scale on the inner side of the leaf sheath at its junction with the blade.
(except most Schismatoglottis spp.); ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals. 1-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
1-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary. ; thecaeThecae: One of the lobes of an anther in which pollen is produced.
dehiscing by apicalApical: Of, relating to, or denoting an apex.
pores, connective not conspicuously thickened
; thecaeThecae: One of the lobes of an anther in which pollen is produced.
dehiscing by apicalApical: Of, relating to, or denoting an apex.
pores, connective not conspicuously thickened
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌47A. | PlacentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta. s parietal; thecaeThecae: One of the lobes of an anther in which pollen is produced.
truncate.
s parietal; thecaeThecae: One of the lobes of an anther in which pollen is produced.
truncate.
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌48A. | SpatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. constricted; ovuleOvule: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells
constricted; ovuleOvule: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells s anatropous to hemianatropous; petiolePetiole: Leaf stem.
s anatropous to hemianatropous; petiolePetiole: Leaf stem. sheath usually not ligulateLigulate: Having a narrow strap-shaped part, especially a membranous scale on the inner side of the leaf sheath at its junction with the blade.
; upper part of spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe.
sheath usually not ligulateLigulate: Having a narrow strap-shaped part, especially a membranous scale on the inner side of the leaf sheath at its junction with the blade.
; upper part of spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe. usually sterile .. 📌49. Schismatoglottis
usually sterile .. 📌49. Schismatoglottis
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | └48B. | SpatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. not constricted; ovuleOvule: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells
not constricted; ovuleOvule: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells s hemiorthotropous to orthotropous; petiolePetiole: Leaf stem.
s hemiorthotropous to orthotropous; petiolePetiole: Leaf stem. sheath with long, marcescentMarcescent: Withering but remaining attached to the stem.
liguleLigule: A narrow strap-shaped part of a plant, especially a membranous scale on the inner side of the leaf sheath at its junction with the blade.
; spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe.
sheath with long, marcescentMarcescent: Withering but remaining attached to the stem.
liguleLigule: A narrow strap-shaped part of a plant, especially a membranous scale on the inner side of the leaf sheath at its junction with the blade.
; spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe. fertile almost to apexApex: End forming a point.
fertile almost to apexApex: End forming a point. .50. 📌Piptospatha
.50. 📌Piptospatha
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ├47B. | PlacentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta. basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
or basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
and apicalApical: Of, relating to, or denoting an apex.
; thecaeThecae: One of the lobes of an anther in which pollen is produced.
truncate or horned
basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
or basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
and apicalApical: Of, relating to, or denoting an apex.
; thecaeThecae: One of the lobes of an anther in which pollen is produced.
truncate or horned
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌49A. | ThecaeThecae: One of the lobes of an anther in which pollen is produced.
truncate; placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta. basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
.51. 📌Hottarum
basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
.51. 📌Hottarum
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ├49B. | ThecaeThecae: One of the lobes of an anther in which pollen is produced.
horned; placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta. basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
or basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
and apicalApical: Of, relating to, or denoting an apex.
basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
or basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
and apicalApical: Of, relating to, or denoting an apex.
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌50A. | StigmaStigma: The receptive tip of a carpel, or of several fused carpels, in the gynoecium of a flower. smaller than ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals.
smaller than ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals. ; upper part of spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe.
; upper part of spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe. sterile with a distinct appendixAppendix: Sterile appendage at the end of a spadix.
sterile with a distinct appendixAppendix: Sterile appendage at the end of a spadix. of hornless sterile flowers; spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
of hornless sterile flowers; spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. constricted or not; stamenStamen: The pollen-producing reproductive organ of a flower.
constricted or not; stamenStamen: The pollen-producing reproductive organ of a flower. s never excavated apicalApical: Of, relating to, or denoting an apex.
ly.
s never excavated apicalApical: Of, relating to, or denoting an apex.
ly.
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌51A. | SpatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. not constricted; male flowers smooth or verrucoseVerrucose: Covered with warts or wartlike projections.
; sterile flowers between male and female flowers flattened .52. 📌Bucephalandra
not constricted; male flowers smooth or verrucoseVerrucose: Covered with warts or wartlike projections.
; sterile flowers between male and female flowers flattened .52. 📌Bucephalandra
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | └51B. | SpatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. constricted; male flowers densely tuberculateTuberculate: Bearing tubercles or warty protuberances.
; sterile flowers between male and female flowers subcylindric .53. 📌Phymatarum
constricted; male flowers densely tuberculateTuberculate: Bearing tubercles or warty protuberances.
; sterile flowers between male and female flowers subcylindric .53. 📌Phymatarum
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ├50B. | StigmaStigma: The receptive tip of a carpel, or of several fused carpels, in the gynoecium of a flower. as broad as ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals.
as broad as ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals. ; upper part of spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe.
; upper part of spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe. mostly fertile to apexApex: End forming a point.
mostly fertile to apexApex: End forming a point. and without a distinct appendixAppendix: Sterile appendage at the end of a spadix.
and without a distinct appendixAppendix: Sterile appendage at the end of a spadix. ; spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
; spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. not conspicuously constricted; stamenStamen: The pollen-producing reproductive organ of a flower.
not conspicuously constricted; stamenStamen: The pollen-producing reproductive organ of a flower. s all or mostly excavated apicalApical: Of, relating to, or denoting an apex.
ly
s all or mostly excavated apicalApical: Of, relating to, or denoting an apex.
ly
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌52A. | StamenStamen: The pollen-producing reproductive organ of a flower. s all excavated; placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta.
s all excavated; placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta. basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
.54. 📌Aridarum
basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
.54. 📌Aridarum
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | └52B. | Two lateral stamenStamen: The pollen-producing reproductive organ of a flower. s of each male flower excavated and thecaeThecae: One of the lobes of an anther in which pollen is produced.
horned, central stamenStamen: The pollen-producing reproductive organ of a flower.
s of each male flower excavated and thecaeThecae: One of the lobes of an anther in which pollen is produced.
horned, central stamenStamen: The pollen-producing reproductive organ of a flower. truncate and thecaeThecae: One of the lobes of an anther in which pollen is produced.
hornless; placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta.
truncate and thecaeThecae: One of the lobes of an anther in which pollen is produced.
hornless; placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta. s basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
(fertile ovuleOvule: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells
s basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
(fertile ovuleOvule: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells s) and apicalApical: Of, relating to, or denoting an apex.
(apparently sterile) .55. 📌Heteroaridarum
s) and apicalApical: Of, relating to, or denoting an apex.
(apparently sterile) .55. 📌Heteroaridarum
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ├40B. | Higher order leaf venationVenation: The arrangement of veins in the leaf. reticulateReticulate: Reticulate Venation.
reticulateReticulate: Reticulate Venation.
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌53A. | Leaf blade dracontioidDracontioid:  , leaf solitary in each growth period
, leaf solitary in each growth period
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌54A. | PetiolePetiole: Leaf stem. usually aculeateAculeate: Sharply pointed; prickly.
; at least some of the ultimate leaf lobes trapezoidTrapezoid:
usually aculeateAculeate: Sharply pointed; prickly.
; at least some of the ultimate leaf lobes trapezoidTrapezoid:  , truncate or shallowly bifid, veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.
, truncate or shallowly bifid, veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.  s not forming regular submarginal collective veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.
s not forming regular submarginal collective veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.  on each side
on each side
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌55A. | PedunclePeduncle: Flower stem. long; ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals.
long; ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals. 1-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
1-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary. .70. 📌Anchomanes
.70. 📌Anchomanes
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | └55B. | PedunclePeduncle: Flower stem. very short; ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals.
very short; ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals. 2-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
2-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary. .71. 📌Pseudohydrosme
.71. 📌Pseudohydrosme
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ├54B. | PetiolePetiole: Leaf stem. usually smooth, sometimes rugoseRugose: Wrinkled; corrugated.
but never aculeateAculeate: Sharply pointed; prickly.
; ultimate leaf lobes usually oblongOblong:
usually smooth, sometimes rugoseRugose: Wrinkled; corrugated.
but never aculeateAculeate: Sharply pointed; prickly.
; ultimate leaf lobes usually oblongOblong:  -ellipticElliptic:
-ellipticElliptic:  , acuminateAcuminate: Tapering to a point.
, with primary lateral veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.
, acuminateAcuminate: Tapering to a point.
, with primary lateral veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.  s forming regular submarginal collective veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.
s forming regular submarginal collective veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.  s on each side
s on each side
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌56A. | OvaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals. 1-4-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
1-4-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary. ; terminal appendixAppendix: Sterile appendage at the end of a spadix.
; terminal appendixAppendix: Sterile appendage at the end of a spadix. smooth, rugoseRugose: Wrinkled; corrugated.
, rarely verrucoseVerrucose: Covered with warts or wartlike projections.
or staminodial (appendixAppendix: Sterile appendage at the end of a spadix.
smooth, rugoseRugose: Wrinkled; corrugated.
, rarely verrucoseVerrucose: Covered with warts or wartlike projections.
or staminodial (appendixAppendix: Sterile appendage at the end of a spadix. absent in Amorphophallus margaritifer and A. coudercii) .79. 📌Amorphophallus
absent in Amorphophallus margaritifer and A. coudercii) .79. 📌Amorphophallus
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | └56B. | OvaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals. always 1-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
always 1-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary. ; terminal appendixAppendix: Sterile appendage at the end of a spadix.
; terminal appendixAppendix: Sterile appendage at the end of a spadix. staminodial, separated from male zone by naked axial region .80. 📌Pseudodracontium
staminodial, separated from male zone by naked axial region .80. 📌Pseudodracontium
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ├53B. | Leaf blade shape of various types but never dracontioidDracontioid:  ; usually several leaves present
; usually several leaves present
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌57A. | SpadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe. fertile to apexApex: End forming a point.
fertile to apexApex: End forming a point. , terminal appendixAppendix: Sterile appendage at the end of a spadix.
, terminal appendixAppendix: Sterile appendage at the end of a spadix. absent
absent
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌58A. | HelophyteHelophyte: A bog plant; especially a perennial marsh plant having its overwintering buds under water.
s with robust, erect stems and an apicalApical: Of, relating to, or denoting an apex.
crown of sagittateSagittate:  to hastateHastate:
to hastateHastate:  (rarely trisect) leaves; tropical America .76. 📌Montrichardia
(rarely trisect) leaves; tropical America .76. 📌Montrichardia
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ├58B. | Terrestrial, hemiepiphyticEpiphytic: A plant that grows harmlessly upon another plant and derives its moisture and nutrients from the air, rain, and sometimes from debris accumulating around it.
or epiphyticEpiphytic: A plant that grows harmlessly upon another plant and derives its moisture and nutrients from the air, rain, and sometimes from debris accumulating around it.
plants, leaf blade variously shaped; tropical Africa.
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌59A. | Leaf blade usually with pellucidPellucid: Translucently clear.
resin canals (lines or points); plants mostly climbing hemiepiphyteEpiphyte: A plant that grows harmlessly upon another plant and derives its moisture and nutrients from the air, rain, and sometimes from debris accumulating around it.
s; spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. boat-shaped, convoluteConvolute: The process of convolute vernation involves the wrapping of one margin of the leaf's blade over the other. This folding mechanism makes the emerging leaf look like a tube.
basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
ly; antherAnther: The part of a stamen that contains the pollen.
boat-shaped, convoluteConvolute: The process of convolute vernation involves the wrapping of one margin of the leaf's blade over the other. This folding mechanism makes the emerging leaf look like a tube.
basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
ly; antherAnther: The part of a stamen that contains the pollen. s lacking endothecial thickenings
s lacking endothecial thickenings
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌60A. | LaticiferLaticifer: A laticifer is a type of elongated secretory cell found in the leaves and/or stems of plants that produce latex and rubber as secondary metabolites.
s absent; flagelliformFlagelliform: Long, slender, and flexible, like the lash of a whip.
shoots absent; leaf blade always simple, acute to rounded at base; ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals. 1-3-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
1-3-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary. ; spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe.
; spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe. stipitateStipitate: Having a stalk or stem.
or sessileSessile: Attached directly by its base without a stalk or peduncle.
.74. 📌Culcasia
stipitateStipitate: Having a stalk or stem.
or sessileSessile: Attached directly by its base without a stalk or peduncle.
.74. 📌Culcasia
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | └60B. | LaticiferLaticifer: A laticifer is a type of elongated secretory cell found in the leaves and/or stems of plants that produce latex and rubber as secondary metabolites.
s present; flagelliformFlagelliform: Long, slender, and flexible, like the lash of a whip.
shoots present; leaf blade oblongOblong:  -lanceolateLanceolate:
-lanceolateLanceolate:  to cordateCordate:
to cordateCordate:  , sagittateSagittate:
, sagittateSagittate:  , hastateHastate:
, hastateHastate:  , trifidTrifid:
, trifidTrifid:  or laciniateLaciniate:
or laciniateLaciniate:  to pinnatifidPinnatifid:
to pinnatifidPinnatifid:  ; ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals.
; ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals. 1-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
1-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary. ; spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe.
; spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe. sessileSessile: Attached directly by its base without a stalk or peduncle.
.75. 📌Cercestis
sessileSessile: Attached directly by its base without a stalk or peduncle.
.75. 📌Cercestis
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ├59B. | Leaf blade lacking pellucidPellucid: Translucently clear.
resin glands; plants terrestrial; spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. ± fully expanded,not convoluteConvolute: The process of convolute vernation involves the wrapping of one margin of the leaf's blade over the other. This folding mechanism makes the emerging leaf look like a tube.
; antherAnther: The part of a stamen that contains the pollen.
± fully expanded,not convoluteConvolute: The process of convolute vernation involves the wrapping of one margin of the leaf's blade over the other. This folding mechanism makes the emerging leaf look like a tube.
; antherAnther: The part of a stamen that contains the pollen. s with endothecial thickenings
s with endothecial thickenings
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌61A. | Leaf cordateCordate:  -sagittateSagittate:
-sagittateSagittate:  or subtriangular, deeply sagittateSagittate:
or subtriangular, deeply sagittateSagittate:  or trifidTrifid:
or trifidTrifid:  , glabrousGlabrous: Smooth. Free from hair or down.
; spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
, glabrousGlabrous: Smooth. Free from hair or down.
; spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. green; spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe.
green; spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe. entirely free of spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
entirely free of spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. .69. 📌Nephthytis
.69. 📌Nephthytis
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | └61B. | Leaf cordateCordate:  -ovateOvate:
-ovateOvate:  , minutely hispidHispid: Covered with stiff hair or bristles.
abaxialAbaxial: Facing away from the stem of a plant (especially denoting the lower surface of a leaf).
ly; spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
, minutely hispidHispid: Covered with stiff hair or bristles.
abaxialAbaxial: Facing away from the stem of a plant (especially denoting the lower surface of a leaf).
ly; spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. pure white; female zone of spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe.
pure white; female zone of spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe. adnateAdnate: Joined by having grown together.
to spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
adnateAdnate: Joined by having grown together.
to spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. .78. 📌Callopsis
.78. 📌Callopsis
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ├57B. | SpadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe. with ± smooth terminal appendixAppendix: Sterile appendage at the end of a spadix.
with ± smooth terminal appendixAppendix: Sterile appendage at the end of a spadix.
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌62A. | LaticiferLaticifer: A laticifer is a type of elongated secretory cell found in the leaves and/or stems of plants that produce latex and rubber as secondary metabolites.
s anastomosingAnastomosing: Connecting with one another, particularly applied to veins.
; tropical South America
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌63A. | OvaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals. 6- to 9-ovulateOvulate: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells
6- to 9-ovulateOvulate: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells ; leaf blade trisect to pedatisect; stem a subgloboseSubglobose: Imperfectly globose ( globe-shaped ).
tuber .58. 📌Zomicarpa
; leaf blade trisect to pedatisect; stem a subgloboseSubglobose: Imperfectly globose ( globe-shaped ).
tuber .58. 📌Zomicarpa
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ├63B. | OvaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals. 1- to 6-ovulateOvulate: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells
1- to 6-ovulateOvulate: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells ; leaf blade cordateCordate:
; leaf blade cordateCordate:  -sagittateSagittate:
-sagittateSagittate:  ; stem a subgloboseSubglobose: Imperfectly globose ( globe-shaped ).
tuber or rhizome
; stem a subgloboseSubglobose: Imperfectly globose ( globe-shaped ).
tuber or rhizome
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌64A. | AppendixAppendix: Sterile appendage at the end of a spadix. slender
slender
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌65A. | StamenStamen: The pollen-producing reproductive organ of a flower. connective much prolonged, thread-like; stem tuberous; ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals.
connective much prolonged, thread-like; stem tuberous; ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals. 1- ovulateOvulate: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells
1- ovulateOvulate: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells .61. 📌Filarum
.61. 📌Filarum
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | └65B. | StamenStamen: The pollen-producing reproductive organ of a flower. connective not at all prolonged; ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals.
connective not at all prolonged; ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals. 1-6-ovulateOvulate: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells
1-6-ovulateOvulate: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells ; stem a creeping rhizome .59. 📌Zomicarpella
; stem a creeping rhizome .59. 📌Zomicarpella
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | └64B. | AppendixAppendix: Sterile appendage at the end of a spadix. relatively thick and subcylindric; stem a creeping rhizome; ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals.
relatively thick and subcylindric; stem a creeping rhizome; ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals. 1-ovulateOvulate: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells
1-ovulateOvulate: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells .60. 📌Ulearum
.60. 📌Ulearum
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ├62B. | LaticiferLaticifer: A laticifer is a type of elongated secretory cell found in the leaves and/or stems of plants that produce latex and rubber as secondary metabolites.
s simple; temperate Eurasia and palaeotropics
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌66A. | SpadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe. with zone of sterile flowers between male and female zones, rarely with a naked axis between female and male zones of spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe.
with zone of sterile flowers between male and female zones, rarely with a naked axis between female and male zones of spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe. (Arum pictum) or with fertile zones contiguous (Dracunculus)
(Arum pictum) or with fertile zones contiguous (Dracunculus)
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌67A. | PlacentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta. parietal to subbasalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
; leaf blade sagittateSagittate:
parietal to subbasalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
; leaf blade sagittateSagittate:  or hastateHastate:
or hastateHastate:  .88. 📌Arum
.88. 📌Arum
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ├67B. | PlacentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta. apicalApical: Of, relating to, or denoting an apex.
and/or basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
; leaf blade variously shaped
apicalApical: Of, relating to, or denoting an apex.
and/or basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
; leaf blade variously shaped
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌68A. | PlacentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta. s basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
and apicalApical: Of, relating to, or denoting an apex.
s basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
and apicalApical: Of, relating to, or denoting an apex.
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌69A. | Male zone of spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe. contiguous with female zone; leaf blade pedatifid but lobes not spirally twisted upwards .90. 📌Dracunculus
contiguous with female zone; leaf blade pedatifid but lobes not spirally twisted upwards .90. 📌Dracunculus
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ├69B. | Male zone of spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe. separated from female zone by subulate to filiform sterile organs; leaf blade variously shaped
separated from female zone by subulate to filiform sterile organs; leaf blade variously shaped
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌70A. | AppendixAppendix: Sterile appendage at the end of a spadix. covered with subulate to setiform sterile flowers; leaf blade pedatifid, lobes twisting upwards on each side .91. 📌Helicodiceros
covered with subulate to setiform sterile flowers; leaf blade pedatifid, lobes twisting upwards on each side .91. 📌Helicodiceros
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | └70B. | AppendixAppendix: Sterile appendage at the end of a spadix. smooth; leaf blade oblongOblong:
smooth; leaf blade oblongOblong:  -lanceolateLanceolate:
-lanceolateLanceolate:  or sagittateSagittate:
or sagittateSagittate:  -hastateHastate:
-hastateHastate:  .92. 📌Theriophonum
.92. 📌Theriophonum
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ├68B. | PlacentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta. basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌71A. | Lower spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. margins free (except Typhonium hirsutum)
margins free (except Typhonium hirsutum)
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌72A. | Infructescence borne above ground level, berries dark red to purple, pericarpPericarp: The part of a fruit formed from the wall of the ripened ovary.
juicy; sterile zone between male and female zones of spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe. relatively long, often partially naked; tropical and subtropical to warm temperate Asia to Australia .93. 📌Typhonium
relatively long, often partially naked; tropical and subtropical to warm temperate Asia to Australia .93. 📌Typhonium
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | └72B. | Infructescence borne at or below ground level, berries white to pale lilac, pericarpPericarp: The part of a fruit formed from the wall of the ripened ovary.
firm, not juicy; sterile zone between male and female zones relatively short and covered entirely with subulate sterile flowers; Turkey, eastern North Africa, Near East, central Asia .89. 📌Eminium
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ├71B. | Lower spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. margins connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
for an appreciable distance (entirely free in Biarum aleppicum)
margins connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
for an appreciable distance (entirely free in Biarum aleppicum)
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌73A. | Leaf usually solitary, blade deeply pedatifid to pedatisect; ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals. 2-several-ovulateOvulate: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells
2-several-ovulateOvulate: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells .94. 📌Sauromatum
.94. 📌Sauromatum
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ├73B. | Leaves several; blade linearLinear:  to ovateOvate:
to ovateOvate:  , ellipticElliptic:
, ellipticElliptic:  or obovateOvate:
or obovateOvate:  ; ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals.
; ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals. 1-ovulateOvulate: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells
1-ovulateOvulate: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌74A. | Leaf blade broadly ellipticElliptic:  , spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
, spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. tube septate .95. 📌Lazarum
tube septate .95. 📌Lazarum
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | └74B. | Leaf blade linearLinear:  , ovateOvate:
, ovateOvate:  , ellipticElliptic:
, ellipticElliptic:  -oblongOblong:
-oblongOblong:  or obovateOvate:
or obovateOvate:  ; spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
; spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. tube not septate .96. 📌Biarum
tube not septate .96. 📌Biarum
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ├66B. | SpadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe. usually without sterile flowers (sometimes present in Arisaema)
usually without sterile flowers (sometimes present in Arisaema)
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌75A. | OvaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals. several-ovulateOvulate: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells
several-ovulateOvulate: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells ; female zone of spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe.
; female zone of spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe. free from spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
free from spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. ; spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
; spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. without a transverse septumSeptum: A partition that separates the locules of a fruit, anther, or sporangium.
separating male and female zones.
without a transverse septumSeptum: A partition that separates the locules of a fruit, anther, or sporangium.
separating male and female zones.
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌76A. | Flowers of both sexes always present in a single inflorescence; male flowers 1-androus; lower spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. margins connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
; leaf blade ovateOvate:
margins connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
; leaf blade ovateOvate:  or sagittateSagittate:
or sagittateSagittate:  .86. 📌Arisarum
.86. 📌Arisarum
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | └76B. | Flowers of both sexes sometimes present in a single inflorescence, but more often with male and female flowers appearing in separate inflorescences; male flowers 2-5-androus; lower spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. margins convoluteConvolute: The process of convolute vernation involves the wrapping of one margin of the leaf's blade over the other. This folding mechanism makes the emerging leaf look like a tube.
; leaf blade normally trisect, pedatisect or radiatisect, rarely simple and ovateOvate:
margins convoluteConvolute: The process of convolute vernation involves the wrapping of one margin of the leaf's blade over the other. This folding mechanism makes the emerging leaf look like a tube.
; leaf blade normally trisect, pedatisect or radiatisect, rarely simple and ovateOvate:  .98. 📌Arisaema
.98. 📌Arisaema
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | └75B. | OvaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals. 1-ovulateOvulate: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells
1-ovulateOvulate: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells ; female zone of spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe.
; female zone of spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe. adnateAdnate: Joined by having grown together.
to spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
adnateAdnate: Joined by having grown together.
to spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. ; spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
; spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. usually with transverse septumSeptum: A partition that separates the locules of a fruit, anther, or sporangium.
between male and female zones .97. 📌Pinellia
usually with transverse septumSeptum: A partition that separates the locules of a fruit, anther, or sporangium.
between male and female zones .97. 📌Pinellia
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ├39B. | SpadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe. entirely enclosed by spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
entirely enclosed by spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. in a basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
"kettle" formed of connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
in a basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
"kettle" formed of connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. margins, plants always helophyticHelophytic: A bog plant; especially a perennial marsh plant having its overwintering buds under water.
or aquatic
margins, plants always helophyticHelophytic: A bog plant; especially a perennial marsh plant having its overwintering buds under water.
or aquatic
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌77A. | Female flowers spirally arranged (pseudo-whorl in Lagenandra nairii, whorled in L. gomezii) and free; spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. tube "kettle" with connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
margins occupying entire spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
tube "kettle" with connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
margins occupying entire spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. tube; spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
tube; spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. blade usually opening only slightly by a straight ot twisted slit; berries free, opening from base; leaf ptyxisPtyxis: The way in which an individual leaf is folded in the bud.
involuteInvolute: In involute vernation both margins on opposing sides of the leaf are rolled up forming two tubes that meet at the midrib of the leaf.
.56. 📌Lagenandra
blade usually opening only slightly by a straight ot twisted slit; berries free, opening from base; leaf ptyxisPtyxis: The way in which an individual leaf is folded in the bud.
involuteInvolute: In involute vernation both margins on opposing sides of the leaf are rolled up forming two tubes that meet at the midrib of the leaf.
.56. 📌Lagenandra
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | └77B. | Female flowers in a single whorl, connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
; spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. tube kettle occupying only lower part of spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
tube kettle occupying only lower part of spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. tube, remainder also with connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
margins (except Cryptocoryne spiralis), blade spreading or twisted; berries connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
into a syncarp which opens from the apexApex: End forming a point.
tube, remainder also with connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
margins (except Cryptocoryne spiralis), blade spreading or twisted; berries connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
into a syncarp which opens from the apexApex: End forming a point. ; leaf ptyxisPtyxis: The way in which an individual leaf is folded in the bud.
convoluteConvolute: The process of convolute vernation involves the wrapping of one margin of the leaf's blade over the other. This folding mechanism makes the emerging leaf look like a tube.
.57. 📌Cryptocoryne
; leaf ptyxisPtyxis: The way in which an individual leaf is folded in the bud.
convoluteConvolute: The process of convolute vernation involves the wrapping of one margin of the leaf's blade over the other. This folding mechanism makes the emerging leaf look like a tube.
.57. 📌Cryptocoryne
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ├38B. | StamenStamen: The pollen-producing reproductive organ of a flower. s of each male flower entirely connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
into a distinct synandriumSynandrium: Sets of stamens of which the anthers have been fused.
, synandriumSynandrium: Sets of stamens of which the anthers have been fused.
rarely reduced to single stamenStamen: The pollen-producing reproductive organ of a flower.
s of each male flower entirely connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
into a distinct synandriumSynandrium: Sets of stamens of which the anthers have been fused.
, synandriumSynandrium: Sets of stamens of which the anthers have been fused.
rarely reduced to single stamenStamen: The pollen-producing reproductive organ of a flower. (Colletogyne endemic to Madagascar) or stamenStamen: The pollen-producing reproductive organ of a flower.
(Colletogyne endemic to Madagascar) or stamenStamen: The pollen-producing reproductive organ of a flower. s free and basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
ly connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
with remote globose thecaeThecae: One of the lobes of an anther in which pollen is produced.
(Gorgonidium endemic to Andean South America), or only filaments connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
and then stigmaStigma: The receptive tip of a carpel, or of several fused carpels, in the gynoecium of a flower.
s free and basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
ly connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
with remote globose thecaeThecae: One of the lobes of an anther in which pollen is produced.
(Gorgonidium endemic to Andean South America), or only filaments connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
and then stigmaStigma: The receptive tip of a carpel, or of several fused carpels, in the gynoecium of a flower. stellate and 5-8-lobed (Spathantheum)
stellate and 5-8-lobed (Spathantheum)
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌78A. | LaticiferLaticifer: A laticifer is a type of elongated secretory cell found in the leaves and/or stems of plants that produce latex and rubber as secondary metabolites.
s simple
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌79A. | SynandriaSynandria: Sets of stamens of which the anthers have been fused.
connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
, thecaeThecae: One of the lobes of an anther in which pollen is produced.
of adjacent synandriaSynandria: Sets of stamens of which the anthers have been fused.
encircling pits in the spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe. , each pit with a somewhat prominent upper margin; leaf peltatePeltate:
, each pit with a somewhat prominent upper margin; leaf peltatePeltate:  ; Burma to India .99. 📌Ariopsis
; Burma to India .99. 📌Ariopsis
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ├79B. | SynandriaSynandria: Sets of stamens of which the anthers have been fused.
free; leaf not peltatePeltate:  ; Africa, Madagascar or Americas
; Africa, Madagascar or Americas
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌80A. | Higher order leaf venationVenation: The arrangement of veins in the leaf. parallel-pinnateParallel-pinnate: Parallel-Pinnate Venation.
parallel-pinnateParallel-pinnate: Parallel-Pinnate Venation. or if reticulateReticulate: Reticulate Venation.
or if reticulateReticulate: Reticulate Venation. then stem a creeping rhizome and plant from Amazonia (Bognera)
then stem a creeping rhizome and plant from Amazonia (Bognera)
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌81A. | OvuleOvule: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells s anatropous; primary lateral veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.
s anatropous; primary lateral veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.  s of leaf forming a single marginal veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.
s of leaf forming a single marginal veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.  , no submarginal collective veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.
, no submarginal collective veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.  present; plant from tropical America or continental tropical Africa.
present; plant from tropical America or continental tropical Africa.
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌82A. | Female zone of spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe. free; plant from tropical west and central Africa .48. 📌Anubias
free; plant from tropical west and central Africa .48. 📌Anubias
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ├82B. | Female zone of spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe. entirely adnateAdnate: Joined by having grown together.
to spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
entirely adnateAdnate: Joined by having grown together.
to spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. ; plant from tropical America.
; plant from tropical America.
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌83A. | Female flowers each with whorl of several staminodeStaminode: A sterile or abortive stamen, frequently resembling a stamen without its anther.
s; higher order leaf venationVenation: The arrangement of veins in the leaf. strictly parallel-pinnateParallel-pinnate: Parallel-Pinnate Venation.
strictly parallel-pinnateParallel-pinnate: Parallel-Pinnate Venation. .35. 📌Dieffenbachia
.35. 📌Dieffenbachia
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | └83B. | Female flowers without staminodeStaminode: A sterile or abortive stamen, frequently resembling a stamen without its anther.
s; higher order leaf venationVenation: The arrangement of veins in the leaf. reticulateReticulate: Reticulate Venation.
reticulateReticulate: Reticulate Venation. .36. 📌Bognera
.36. 📌Bognera
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ├81B. | OvuleOvule: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells s orthotropous to hemi-orthotropous; primary lateral veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.
s orthotropous to hemi-orthotropous; primary lateral veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.  s of leaf forming submarginal collective veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.
s of leaf forming submarginal collective veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.  and 1-2 marginal veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.
and 1-2 marginal veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.  s; plants from temperate eastern North America or Madagascar.
s; plants from temperate eastern North America or Madagascar.
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌84A. | Giant herbs (to 4m) with massive pseudostem of petiolePetiole: Leaf stem. sheaths; staminodeStaminode: A sterile or abortive stamen, frequently resembling a stamen without its anther.
s of female flower free; Madagascar (also naturalized in Pemba, Zanzibar and Mascarene Is.) .85. 📌Typhonodorum
sheaths; staminodeStaminode: A sterile or abortive stamen, frequently resembling a stamen without its anther.
s of female flower free; Madagascar (also naturalized in Pemba, Zanzibar and Mascarene Is.) .85. 📌Typhonodorum
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | └84B. | Relatively small herbs (less than 1m) without pseudostem; staminodeStaminode: A sterile or abortive stamen, frequently resembling a stamen without its anther.
s of female flower connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
into a cup-like synandrodium; eastern North America .84. 📌Peltandra
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ├80B. | Higher order leaf venationVenation: The arrangement of veins in the leaf. reticulateReticulate: Reticulate Venation.
reticulateReticulate: Reticulate Venation. ; stem usually a subgloboseSubglobose: Imperfectly globose ( globe-shaped ).
tuber, if rhizomatous then plant Madagascan
; stem usually a subgloboseSubglobose: Imperfectly globose ( globe-shaped ).
tuber, if rhizomatous then plant Madagascan
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌85A. | Madagascan plants; seed lacking endospermEndosperm: A tissue produced inside the seeds of most of the flowering plants following fertilization. It surrounds the embryo and provides nutrition in the form of starch, though it can also contain oils and protein.
; ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals. 1-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
1-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary. ; leaf venationVenation: The arrangement of veins in the leaf.
; leaf venationVenation: The arrangement of veins in the leaf. with primary lateral veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.
with primary lateral veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.  s forming submarginal collective veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.
s forming submarginal collective veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.  and 1-2 marginal veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.
and 1-2 marginal veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.  s on each side of blade
s on each side of blade
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌86A. | StamenStamen: The pollen-producing reproductive organ of a flower. s either completely connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
with marginal thecaeThecae: One of the lobes of an anther in which pollen is produced.
or only partially connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
by filaments; bisexual flowers often present between male and female zones of the spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe.
s either completely connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
with marginal thecaeThecae: One of the lobes of an anther in which pollen is produced.
or only partially connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
by filaments; bisexual flowers often present between male and female zones of the spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe. .82. 📌Carlephyton
.82. 📌Carlephyton
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ├86B. | StamenStamen: The pollen-producing reproductive organ of a flower. s completely connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
into truncate synandriaSynandria: Sets of stamens of which the anthers have been fused.
or synandriaSynandria: Sets of stamens of which the anthers have been fused.
reduced to one stamenStamen: The pollen-producing reproductive organ of a flower.
s completely connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
into truncate synandriaSynandria: Sets of stamens of which the anthers have been fused.
or synandriaSynandria: Sets of stamens of which the anthers have been fused.
reduced to one stamenStamen: The pollen-producing reproductive organ of a flower.
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌87A. | SynandriaSynandria: Sets of stamens of which the anthers have been fused.
reduced to one stamenStamen: The pollen-producing reproductive organ of a flower. , thecaeThecae: One of the lobes of an anther in which pollen is produced.
apicalApical: Of, relating to, or denoting an apex.
on conical filament; spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe.
, thecaeThecae: One of the lobes of an anther in which pollen is produced.
apicalApical: Of, relating to, or denoting an apex.
on conical filament; spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe. fertile to apexApex: End forming a point.
fertile to apexApex: End forming a point. ; leaf blade always cordateCordate:
; leaf blade always cordateCordate:  .83. 📌Colletogyne
.83. 📌Colletogyne
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | └87B. | ThecaeThecae: One of the lobes of an anther in which pollen is produced.
apicalApical: Of, relating to, or denoting an apex.
on a truncate synandriumSynandrium: Sets of stamens of which the anthers have been fused.
; spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe. appendixAppendix: Sterile appendage at the end of a spadix.
appendixAppendix: Sterile appendage at the end of a spadix. present or not; leaf blade cordateCordate:
present or not; leaf blade cordateCordate:  , hastateHastate:
, hastateHastate:  , trifidTrifid:
, trifidTrifid:  , trisect or pedatifid .81. 📌Arophyton
, trisect or pedatifid .81. 📌Arophyton
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ├85B. | South American plants; seed with abundant endospermEndosperm: A tissue produced inside the seeds of most of the flowering plants following fertilization. It surrounds the embryo and provides nutrition in the form of starch, though it can also contain oils and protein.
; ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals. with more than 1 loculeLocule: A small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
with more than 1 loculeLocule: A small cavity or compartment within an ovary. (except Spathicarpa); leaf venationVenation: The arrangement of veins in the leaf.
(except Spathicarpa); leaf venationVenation: The arrangement of veins in the leaf. with primary lateral veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.
with primary lateral veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.  s usually forming single marginal veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.
s usually forming single marginal veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.  on each side, submarginal collective veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.
on each side, submarginal collective veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.  s usually absent
s usually absent
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌88A. | SpadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe. free or only female zone adnateAdnate: Joined by having grown together.
to spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
free or only female zone adnateAdnate: Joined by having grown together.
to spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌89A. | OvuleOvule: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells s anatropous
s anatropous
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌90A. | OvuleOvule: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells s 2 per loculeLocule: A small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
s 2 per loculeLocule: A small cavity or compartment within an ovary. ; leaf blade entire, linearLinear:
; leaf blade entire, linearLinear:  to subsagittateSagittate:
to subsagittateSagittate:  ; spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe.
; spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe. , with terminal appendixAppendix: Sterile appendage at the end of a spadix.
, with terminal appendixAppendix: Sterile appendage at the end of a spadix. of synandrodeSynandrode: A set of fused sterile stamens.
s .37. 📌Mangonia
of synandrodeSynandrode: A set of fused sterile stamens.
s .37. 📌Mangonia
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ├90B. | OvuleOvule: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells s 1 per loculeLocule: A small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
s 1 per loculeLocule: A small cavity or compartment within an ovary. ; leaf blade entire, pinnatifidPinnatifid:
; leaf blade entire, pinnatifidPinnatifid:  to subdracontioidDracontioid:
to subdracontioidDracontioid:  ; spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe.
; spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe. fertile to apexApex: End forming a point.
fertile to apexApex: End forming a point.
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌91A. | Leaf blade pinnatifidPinnatifid:  to bipinnatifidPinnatifid:
to bipinnatifidPinnatifid:  or subdracontioidDracontioid:
or subdracontioidDracontioid:  ; synandriaSynandria: Sets of stamens of which the anthers have been fused.
elongate; stigmaStigma: The receptive tip of a carpel, or of several fused carpels, in the gynoecium of a flower.
; synandriaSynandria: Sets of stamens of which the anthers have been fused.
elongate; stigmaStigma: The receptive tip of a carpel, or of several fused carpels, in the gynoecium of a flower. capitate or lobed; staminodeStaminode: A sterile or abortive stamen, frequently resembling a stamen without its anther.
s of female flowers free (connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
in Taccarum caudatum) .38. 📌Taccarum
capitate or lobed; staminodeStaminode: A sterile or abortive stamen, frequently resembling a stamen without its anther.
s of female flowers free (connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
in Taccarum caudatum) .38. 📌Taccarum
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | └91B. | Leaf blade usually pinnatifidPinnatifid:  , rarely entire; synandriaSynandria: Sets of stamens of which the anthers have been fused.
short and domed; stigmaStigma: The receptive tip of a carpel, or of several fused carpels, in the gynoecium of a flower.
, rarely entire; synandriaSynandria: Sets of stamens of which the anthers have been fused.
short and domed; stigmaStigma: The receptive tip of a carpel, or of several fused carpels, in the gynoecium of a flower. deeply lobed; staminodeStaminode: A sterile or abortive stamen, frequently resembling a stamen without its anther.
s of female flowers free or connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
.39. 📌Asterostigma
deeply lobed; staminodeStaminode: A sterile or abortive stamen, frequently resembling a stamen without its anther.
s of female flowers free or connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
.39. 📌Asterostigma
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ├89B. | OvuleOvule: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells s orthotropous
s orthotropous
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌92A. | StyleStyle: The usually slender part of a pistil, connecting the ovary and the stigma. s and synandriaSynandria: Sets of stamens of which the anthers have been fused.
elongate; leaf blade pinnatifidPinnatifid:
s and synandriaSynandria: Sets of stamens of which the anthers have been fused.
elongate; leaf blade pinnatifidPinnatifid:  or -sect or bipinnatifidPinnatifid:
or -sect or bipinnatifidPinnatifid:  or entire and ± cordateCordate:
or entire and ± cordateCordate: 
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌93A. | StaminodeStaminode: A sterile or abortive stamen, frequently resembling a stamen without its anther.
s in female flowers filiform to subclavateClavate: Club-shaped; thicker at the apex than at the base.
; synandriaSynandria: Sets of stamens of which the anthers have been fused.
with free filament apicesApices: Plural of apex. End forming a point. or not; leaf blade pinnatifidPinnatifid:
or not; leaf blade pinnatifidPinnatifid:  , pinnatisectPinnatisect: Having lobes with incisions that extend almost, or up to midrib.
, pinnatisectPinnatisect: Having lobes with incisions that extend almost, or up to midrib. or bipinnatifidPinnatifid:
or bipinnatifidPinnatifid:  .40. 📌Gorgonidium
.40. 📌Gorgonidium
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | └93B. | StaminodeStaminode: A sterile or abortive stamen, frequently resembling a stamen without its anther.
s in female flowers elongate-triangular; synandriaSynandria: Sets of stamens of which the anthers have been fused.
entirely connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
; leaf blade entire, ± cordateCordate:  .41. 📌Synandrospadix
.41. 📌Synandrospadix
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | └92B. | StyleStyle: The usually slender part of a pistil, connecting the ovary and the stigma. s and synandriaSynandria: Sets of stamens of which the anthers have been fused.
short and squat or synandriaSynandria: Sets of stamens of which the anthers have been fused.
very flat; staminodeStaminode: A sterile or abortive stamen, frequently resembling a stamen without its anther.
s in female flowers obovateOvate:
s and synandriaSynandria: Sets of stamens of which the anthers have been fused.
short and squat or synandriaSynandria: Sets of stamens of which the anthers have been fused.
very flat; staminodeStaminode: A sterile or abortive stamen, frequently resembling a stamen without its anther.
s in female flowers obovateOvate:  or trapezoidTrapezoid:
or trapezoidTrapezoid:  ; leaf blade pedatisect or subpalmatifid .42. 📌Gearum
; leaf blade pedatisect or subpalmatifid .42. 📌Gearum
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ├88B. | SpadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe. usually entirely adnateAdnate: Joined by having grown together.
to spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
usually entirely adnateAdnate: Joined by having grown together.
to spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. (male zone free in Spathantheum intermedium)
(male zone free in Spathantheum intermedium)
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌94A. | OvaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals. 6-8-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
6-8-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary. ; female flowers below, male above; leaf blade entire or pinnatePinnate: Pinnate Venation.
; female flowers below, male above; leaf blade entire or pinnatePinnate: Pinnate Venation. ly lobed .43. 📌Spathantheum
ly lobed .43. 📌Spathantheum
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | └94B. | OvaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals. 1-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
1-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary. ; female and male flowers intermixed (2 central rows of male flowers, 2 outer rows of female flowers); leaf blade entire.44. 📌Spathicarpa
; female and male flowers intermixed (2 central rows of male flowers, 2 outer rows of female flowers); leaf blade entire.44. 📌Spathicarpa
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ├78B. | LaticiferLaticifer: A laticifer is a type of elongated secretory cell found in the leaves and/or stems of plants that produce latex and rubber as secondary metabolites.
s anastomosingAnastomosing: Connecting with one another, particularly applied to veins.
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌95A. | Plants climbing hemiepiphyteEpiphyte: A plant that grows harmlessly upon another plant and derives its moisture and nutrients from the air, rain, and sometimes from debris accumulating around it.
s, sometimes creeping on ground in submature growth; internodes long; berries connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
into a syncarp .67. 📌Syngonium
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ├95B. | Plants terrestrial or geophytic, rarely aquatic, not climbing; internodes very short; berries free from each other
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌96A. | SpadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe. without an appendixAppendix: Sterile appendage at the end of a spadix.
without an appendixAppendix: Sterile appendage at the end of a spadix. (present in Hapaline appendiculata, included here, occasionally absent in Colocasia esculenta, excluded here)
(present in Hapaline appendiculata, included here, occasionally absent in Colocasia esculenta, excluded here)
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌97A. | OvaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals. completely to incompletely 2- to several-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
completely to incompletely 2- to several-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary. with deeply intrusive parietal placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta.
with deeply intrusive parietal placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta. s (1-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
s (1-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary. with basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta.
with basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta. in Jasarum, Scaphispatha and a few species of Caladium and Xanthosoma); neotropical plants
in Jasarum, Scaphispatha and a few species of Caladium and Xanthosoma); neotropical plants
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌98A. | HelophyteHelophyte: A bog plant; especially a perennial marsh plant having its overwintering buds under water.
s or terrestrial; leaf blade ovateOvate:  , sagittateSagittate:
, sagittateSagittate:  to hastateHastate:
to hastateHastate:  or pedatifid
or pedatifid
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌99A. | Pollen shed in tetrads; styleStyle: The usually slender part of a pistil, connecting the ovary and the stigma. usually laterally thickened or expanded into a diaphanous mantle; leaf blade rarely peltatePeltate:
usually laterally thickened or expanded into a diaphanous mantle; leaf blade rarely peltatePeltate:  , sometimes trifidTrifid:
, sometimes trifidTrifid:  or -sect, or pedatifid or -sect
or -sect, or pedatifid or -sect
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌100A. | SpatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. tube subgloboseSubglobose: Imperfectly globose ( globe-shaped ).
, inflated; female zone of spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe.
tube subgloboseSubglobose: Imperfectly globose ( globe-shaped ).
, inflated; female zone of spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe. free; styleStyle: The usually slender part of a pistil, connecting the ovary and the stigma.
free; styleStyle: The usually slender part of a pistil, connecting the ovary and the stigma. s normally discoid (laterally swollen) and coherent (except Xanthosoma plowmanii); synandrodeSynandrode: A set of fused sterile stamens.
s (sterile flowers) between male and female flowers well-developed, ± prismatic .65. 📌Xanthosoma
s normally discoid (laterally swollen) and coherent (except Xanthosoma plowmanii); synandrodeSynandrode: A set of fused sterile stamens.
s (sterile flowers) between male and female flowers well-developed, ± prismatic .65. 📌Xanthosoma
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | └100B. | SpatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. tube narrow, elongate; female zone of spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe.
tube narrow, elongate; female zone of spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe. mostly adnateAdnate: Joined by having grown together.
to spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
mostly adnateAdnate: Joined by having grown together.
to spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. ; stylarStylar: The usually slender part of a pistil, connecting the ovary and the stigma.
; stylarStylar: The usually slender part of a pistil, connecting the ovary and the stigma. region thin, spreading, diaphanous, mantle-like; synandrodeSynandrode: A set of fused sterile stamens.
s (sterile flowers) betweeen male and female flowers usually irregular or fungiform, not prismatic .66. 📌Chlorospatha
region thin, spreading, diaphanous, mantle-like; synandrodeSynandrode: A set of fused sterile stamens.
s (sterile flowers) betweeen male and female flowers usually irregular or fungiform, not prismatic .66. 📌Chlorospatha
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ├99B. | Pollen shed in monads; stylarStylar: The usually slender part of a pistil, connecting the ovary and the stigma. region not laterally expanded; leaf blade usually peltatePeltate:
region not laterally expanded; leaf blade usually peltatePeltate:  , rarely trisect, never pedatifid or -sect
, rarely trisect, never pedatifid or -sect
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌101A. | SpatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. tube always convoluteConvolute: The process of convolute vernation involves the wrapping of one margin of the leaf's blade over the other. This folding mechanism makes the emerging leaf look like a tube.
; stylarStylar: The usually slender part of a pistil, connecting the ovary and the stigma.
tube always convoluteConvolute: The process of convolute vernation involves the wrapping of one margin of the leaf's blade over the other. This folding mechanism makes the emerging leaf look like a tube.
; stylarStylar: The usually slender part of a pistil, connecting the ovary and the stigma. region as broad as ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals.
region as broad as ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals. (Caladium paradoxum has discoid, coherent stylarStylar: The usually slender part of a pistil, connecting the ovary and the stigma.
(Caladium paradoxum has discoid, coherent stylarStylar: The usually slender part of a pistil, connecting the ovary and the stigma. regions); synandrodeSynandrode: A set of fused sterile stamens.
s (sterile flowers) between male and female flowers well-developed, prismatic; placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta.
regions); synandrodeSynandrode: A set of fused sterile stamens.
s (sterile flowers) between male and female flowers well-developed, prismatic; placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta. s 1-2(-3), parietal; seeds several (rarely 1-2) .63. 📌Caladium
s 1-2(-3), parietal; seeds several (rarely 1-2) .63. 📌Caladium
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | └101B. | SpatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. tube gaping widely at anthesisAnthesis: The period during which pollen is presented and/or the stigma is receptive.
; styleStyle: The usually slender part of a pistil, connecting the ovary and the stigma.
tube gaping widely at anthesisAnthesis: The period during which pollen is presented and/or the stigma is receptive.
; styleStyle: The usually slender part of a pistil, connecting the ovary and the stigma. much narrower than ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals.
much narrower than ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals. ; synandrodeSynandrode: A set of fused sterile stamens.
s (sterile flowers) lacking, male and female zones contiguous; placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta.
; synandrodeSynandrode: A set of fused sterile stamens.
s (sterile flowers) lacking, male and female zones contiguous; placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta. 1, basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
; seed solitary .62. 📌Scaphispatha
1, basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
; seed solitary .62. 📌Scaphispatha
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | └98B. | Submerged aquatics; leaf blade linearLinear:  .64. 📌Jasarum
.64. 📌Jasarum
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ├97B. | OvaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals. clearly 1-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
clearly 1-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary. , placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta.
, placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta. s not intrusive; palaeotropical plants
s not intrusive; palaeotropical plants
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌102A. | OvuleOvule: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells s more than 1; leaf blade peltatePeltate:
s more than 1; leaf blade peltatePeltate: 
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌103A. | Female flowers with staminodeStaminode: A sterile or abortive stamen, frequently resembling a stamen without its anther.
s; spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. not constricted; stem trunk-like or creeping .101. 📌Steudnera
not constricted; stem trunk-like or creeping .101. 📌Steudnera
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | └103B. | Female flowers without staminodeStaminode: A sterile or abortive stamen, frequently resembling a stamen without its anther.
s; spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. with 1 or 2 constrictions; stem tuberous, producing erect or spreading stolons bearing small tubercles covered in hooked scales .102. 📌Remusatia
with 1 or 2 constrictions; stem tuberous, producing erect or spreading stolons bearing small tubercles covered in hooked scales .102. 📌Remusatia
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | └102B. | OvuleOvule: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells solitary; leaf blade not peltatePeltate:
solitary; leaf blade not peltatePeltate:  .68. 📌Hapaline
.68. 📌Hapaline
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ├96B. | SpadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe. with an appendixAppendix: Sterile appendage at the end of a spadix.
with an appendixAppendix: Sterile appendage at the end of a spadix. (occasionally absent in Colocasia esculenta); palaeotropical plants
(occasionally absent in Colocasia esculenta); palaeotropical plants
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌104A. | Leaf blade pedatisect to radiatisect; female flowers each with several large staminodeStaminode: A sterile or abortive stamen, frequently resembling a stamen without its anther.
s .100. 📌Protarum
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ├104B. | Leaf blade entire or pinnatifidPinnatifid:  ; female flowers without staminodeStaminode: A sterile or abortive stamen, frequently resembling a stamen without its anther.
s (except single small ones in Colocasia esculenta)
; female flowers without staminodeStaminode: A sterile or abortive stamen, frequently resembling a stamen without its anther.
s (except single small ones in Colocasia esculenta)
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | ┌105A. | PlacentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta. s parietal; ovuleOvule: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells
s parietal; ovuleOvule: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells s many; leaf blade always entire .103. 📌Colocasia
s many; leaf blade always entire .103. 📌Colocasia
|
| │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | │ | └105B. | PlacentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta. basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
; ovuleOvule: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells
basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
; ovuleOvule: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells s few; leaf blade entire or pinnatifidPinnatifid:
s few; leaf blade entire or pinnatifidPinnatifid:  .104. 📌Alocasia
.104. 📌Alocasia
|
 and blade, primary venationVenation: The arrangement of veins in the leaf.
and blade, primary venationVenation: The arrangement of veins in the leaf. strictly parallelParallel: Parallel Venation.
strictly parallelParallel: Parallel Venation. ; inflorescence borne on a culm-like axis
; inflorescence borne on a culm-like axis solitary, pseudolateral and overtopped by a single, erect, leaf-like spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
solitary, pseudolateral and overtopped by a single, erect, leaf-like spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. ; flowers 3-merous, tepalTepal: A segment of the outer whorl in a flower that has no differentiation between petals and sepals.
s .6. 📌Acorus (Acoraceae)
; flowers 3-merous, tepalTepal: A segment of the outer whorl in a flower that has no differentiation between petals and sepals.
s .6. 📌Acorus (Acoraceae) and expanded blade, primary venationVenation: The arrangement of veins in the leaf.
and expanded blade, primary venationVenation: The arrangement of veins in the leaf. never strictly parallelParallel: Parallel Venation.
never strictly parallelParallel: Parallel Venation.
 leaf, tuberous stem and boat-shaped, fornicateFornicate: Arched or bending over.
spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
leaf, tuberous stem and boat-shaped, fornicateFornicate: Arched or bending over.
spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. - see lead 22)
- see lead 22) uniform in appearance with flowers of only one type
uniform in appearance with flowers of only one type parallel-pinnateParallel-pinnate: Parallel-Pinnate Venation.
parallel-pinnateParallel-pinnate: Parallel-Pinnate Venation. ; tissues with abundant trichosclereidTrichosclereid: A hard, needle-like branched cell.
s
; tissues with abundant trichosclereidTrichosclereid: A hard, needle-like branched cell.
s persistentPersistent: Remaining attached to the plant beyond the usual time of falling.
; tepalTepal: A segment of the outer whorl in a flower that has no differentiation between petals and sepals.
s free or connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
; ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals.
persistentPersistent: Remaining attached to the plant beyond the usual time of falling.
; tepalTepal: A segment of the outer whorl in a flower that has no differentiation between petals and sepals.
s free or connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
; ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals. 2-4-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
2-4-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary. ; ovuleOvule: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells
; ovuleOvule: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells s 2-8 per loculeLocule: A small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
s 2-8 per loculeLocule: A small cavity or compartment within an ovary. , placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta.
, placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta. axile .9. 📌Spathiphyllum
axile .9. 📌Spathiphyllum deliquescentDeliquescent: Having a tendency to become liquid.
; tepalTepal: A segment of the outer whorl in a flower that has no differentiation between petals and sepals.
s connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
; ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals.
deliquescentDeliquescent: Having a tendency to become liquid.
; tepalTepal: A segment of the outer whorl in a flower that has no differentiation between petals and sepals.
s connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
; ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals. 1-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
1-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary. ; ovuleOvule: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells
; ovuleOvule: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells s several, placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta.
s several, placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta. basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
.10. 📌Holochlamys
basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
.10. 📌Holochlamys clearly reticulateReticulate: Reticulate Venation.
clearly reticulateReticulate: Reticulate Venation. d; tissues without trichosclereidTrichosclereid: A hard, needle-like branched cell.
s or trichosclereidTrichosclereid: A hard, needle-like branched cell.
s very few
d; tissues without trichosclereidTrichosclereid: A hard, needle-like branched cell.
s or trichosclereidTrichosclereid: A hard, needle-like branched cell.
s very few transversely oblongOblong:
transversely oblongOblong:  ; stamenStamen: The pollen-producing reproductive organ of a flower.
; stamenStamen: The pollen-producing reproductive organ of a flower. s always 4 per flower; pollen inaperturateInaperturate: Without an opening.
; perigonePerigone: The outer part of a flower, consisting of the calyx (sepals) and corolla (petals).
consisting of a single cup-like structure .11. 📌Anadendrum
s always 4 per flower; pollen inaperturateInaperturate: Without an opening.
; perigonePerigone: The outer part of a flower, consisting of the calyx (sepals) and corolla (petals).
consisting of a single cup-like structure .11. 📌Anadendrum hemispheric to discoid; stamenStamen: The pollen-producing reproductive organ of a flower.
hemispheric to discoid; stamenStamen: The pollen-producing reproductive organ of a flower. s usually 6 per flower; pollen monosulcateSulcate: Furrowed; grooved.
; perigonePerigone: The outer part of a flower, consisting of the calyx (sepals) and corolla (petals).
usually consisting of free tepalTepal: A segment of the outer whorl in a flower that has no differentiation between petals and sepals.
s or when connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
and cup-like the flowers are borne on short pedicels
s usually 6 per flower; pollen monosulcateSulcate: Furrowed; grooved.
; perigonePerigone: The outer part of a flower, consisting of the calyx (sepals) and corolla (petals).
usually consisting of free tepalTepal: A segment of the outer whorl in a flower that has no differentiation between petals and sepals.
s or when connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
and cup-like the flowers are borne on short pedicels 3-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
3-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary. ; loculeLocule: A small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
; loculeLocule: A small cavity or compartment within an ovary. s 1-ovulateOvulate: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells
s 1-ovulateOvulate: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells ; flowering shoot with inflorescences always axillary
; flowering shoot with inflorescences always axillary 1-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
1-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary. ; flowering shoots terminating in a branching system of spadices .7. 📌Pothoidium
; flowering shoots terminating in a branching system of spadices .7. 📌Pothoidium to ellipticElliptic:
to ellipticElliptic: 
 2-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
2-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary. ; ovuleOvule: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells
; ovuleOvule: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells s 2 per loculeLocule: A small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
s 2 per loculeLocule: A small cavity or compartment within an ovary. , placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta.
, placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta. axile .3. 📌Lysichiton
axile .3. 📌Lysichiton 1-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
1-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary. ; ovuleOvule: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells
; ovuleOvule: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells 1, placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta.
1, placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta. apicalApical: Of, relating to, or denoting an apex.
or basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
apicalApical: Of, relating to, or denoting an apex.
or basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
 basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
; spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
; spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. inconspicuous; spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe.
inconspicuous; spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe. cylindric, stipeStipe: A stalk or stem.
very long .2. 📌Orontium
cylindric, stipeStipe: A stalk or stem.
very long .2. 📌Orontium apicalApical: Of, relating to, or denoting an apex.
; spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
apicalApical: Of, relating to, or denoting an apex.
; spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. thick, ventricoseVentricose: Distended, inflated. Having a protruding belly.
, enclosing spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe.
thick, ventricoseVentricose: Distended, inflated. Having a protruding belly.
, enclosing spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe. ; spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe.
; spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe. subgloboseSubglobose: Imperfectly globose ( globe-shaped ).
, stipeStipe: A stalk or stem.
short .4. 📌Symplocarpus
subgloboseSubglobose: Imperfectly globose ( globe-shaped ).
, stipeStipe: A stalk or stem.
short .4. 📌Symplocarpus , pinnatifidPinnatifid:
, pinnatifidPinnatifid:  , pinnatisectPinnatisect: Having lobes with incisions that extend almost, or up to midrib.
, pinnatisectPinnatisect: Having lobes with incisions that extend almost, or up to midrib. or dracontioidDracontioid:
or dracontioidDracontioid: 
 , anteriorAnterior:
, anteriorAnterior:  division not pinnatifidPinnatifid:
division not pinnatifidPinnatifid:  or pinnatisectPinnatisect: Having lobes with incisions that extend almost, or up to midrib.
or pinnatisectPinnatisect: Having lobes with incisions that extend almost, or up to midrib.
 many- to 2-ovulateOvulate: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells
many- to 2-ovulateOvulate: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells , rarely 1-ovulateOvulate: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells
, rarely 1-ovulateOvulate: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells ; seeds with endospermEndosperm: A tissue produced inside the seeds of most of the flowering plants following fertilization. It surrounds the embryo and provides nutrition in the form of starch, though it can also contain oils and protein.
; seeds with endospermEndosperm: A tissue produced inside the seeds of most of the flowering plants following fertilization. It surrounds the embryo and provides nutrition in the form of starch, though it can also contain oils and protein.
 spines dispersed; stamenStamen: The pollen-producing reproductive organ of a flower.
spines dispersed; stamenStamen: The pollen-producing reproductive organ of a flower. filaments free; tropical Asia to Oceania .26. 📌Cyrtosperma
filaments free; tropical Asia to Oceania .26. 📌Cyrtosperma spines in ridges; stamenStamen: The pollen-producing reproductive organ of a flower.
spines in ridges; stamenStamen: The pollen-producing reproductive organ of a flower. filaments free or connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
; tropical West Africa .27. 📌Lasimorpha
filaments free or connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
; tropical West Africa .27. 📌Lasimorpha 1-ovulateOvulate: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells
1-ovulateOvulate: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells , rarely 2-ovulateOvulate: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells
, rarely 2-ovulateOvulate: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells ; seeds without endospermEndosperm: A tissue produced inside the seeds of most of the flowering plants following fertilization. It surrounds the embryo and provides nutrition in the form of starch, though it can also contain oils and protein.
or rarely with a little endospermEndosperm: A tissue produced inside the seeds of most of the flowering plants following fertilization. It surrounds the embryo and provides nutrition in the form of starch, though it can also contain oils and protein.
; seeds without endospermEndosperm: A tissue produced inside the seeds of most of the flowering plants following fertilization. It surrounds the embryo and provides nutrition in the form of starch, though it can also contain oils and protein.
or rarely with a little endospermEndosperm: A tissue produced inside the seeds of most of the flowering plants following fertilization. It surrounds the embryo and provides nutrition in the form of starch, though it can also contain oils and protein.
 aculeateAculeate: Sharply pointed; prickly.
, with obvious spines; Malay Archipelago .28. 📌Podolasia
aculeateAculeate: Sharply pointed; prickly.
, with obvious spines; Malay Archipelago .28. 📌Podolasia smooth to scabrid-verrucoseVerrucose: Covered with warts or wartlike projections.
, never aculeateAculeate: Sharply pointed; prickly.
; tropical America
smooth to scabrid-verrucoseVerrucose: Covered with warts or wartlike projections.
, never aculeateAculeate: Sharply pointed; prickly.
; tropical America lanceolateLanceolate:
lanceolateLanceolate:  , very long-acuminateAcuminate: Tapering to a point.
and usually spirally twisted; ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals.
, very long-acuminateAcuminate: Tapering to a point.
and usually spirally twisted; ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals. loculeLocule: A small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
loculeLocule: A small cavity or compartment within an ovary. s with (1-)2 to several ovuleOvule: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells
s with (1-)2 to several ovuleOvule: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells s; neotropics .30. 📌Urospatha
s; neotropics .30. 📌Urospatha s; spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
s; spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. fornicateFornicate: Arched or bending over.
; endemic to Brazil (coastal Bahia and Espirito Santo) .22. 📌Dracontioides
fornicateFornicate: Arched or bending over.
; endemic to Brazil (coastal Bahia and Espirito Santo) .22. 📌Dracontioides , pinnatisectPinnatisect: Having lobes with incisions that extend almost, or up to midrib.
, pinnatisectPinnatisect: Having lobes with incisions that extend almost, or up to midrib. , dracontioidDracontioid:
, dracontioidDracontioid:  or sometimes ± pedatifid; anteriorAnterior:
or sometimes ± pedatifid; anteriorAnterior:  division always pinnatePinnate: Pinnate Venation.
division always pinnatePinnate: Pinnate Venation. ly divided, either pinnatifidPinnatifid:
ly divided, either pinnatifidPinnatifid:  , pinnatisectPinnatisect: Having lobes with incisions that extend almost, or up to midrib.
, pinnatisectPinnatisect: Having lobes with incisions that extend almost, or up to midrib. or yet more highly divided
or yet more highly divided , anteriorAnterior:
, anteriorAnterior:  division bipinnatifidPinnatifid:
division bipinnatifidPinnatifid:  or yet more highly divided; stem a depressed-globose tuber; spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
or yet more highly divided; stem a depressed-globose tuber; spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. fornicateFornicate: Arched or bending over.
fornicateFornicate: Arched or bending over.
 , pinnatisectPinnatisect: Having lobes with incisions that extend almost, or up to midrib.
, pinnatisectPinnatisect: Having lobes with incisions that extend almost, or up to midrib. , or sometimes ± pedatifid, anteriorAnterior:
, or sometimes ± pedatifid, anteriorAnterior:  division pinnatifidPinnatifid:
division pinnatifidPinnatifid:  to pinnatisectPinnatisect: Having lobes with incisions that extend almost, or up to midrib.
to pinnatisectPinnatisect: Having lobes with incisions that extend almost, or up to midrib. ; stem a vertical or horizontal rhizome; spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
; stem a vertical or horizontal rhizome; spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. erect, not fornicateFornicate: Arched or bending over.
, blade often spirally twisted apicalApical: Of, relating to, or denoting an apex.
ly
erect, not fornicateFornicate: Arched or bending over.
, blade often spirally twisted apicalApical: Of, relating to, or denoting an apex.
ly clearly divided into basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
female zone and apicalApical: Of, relating to, or denoting an apex.
male zone; tropical Africa
clearly divided into basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
female zone and apicalApical: Of, relating to, or denoting an apex.
male zone; tropical Africa to tri- or quadripinnatifidPinnatifid:
to tri- or quadripinnatifidPinnatifid:  ; tepalTepal: A segment of the outer whorl in a flower that has no differentiation between petals and sepals.
s free; spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
; tepalTepal: A segment of the outer whorl in a flower that has no differentiation between petals and sepals.
s free; spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. margins free
margins free ; stamenStamen: The pollen-producing reproductive organ of a flower.
; stamenStamen: The pollen-producing reproductive organ of a flower. s free .32. 📌Zamioculcas
s free .32. 📌Zamioculcas to quadripinnatifidPinnatifid:
to quadripinnatifidPinnatifid:  , at least in lowest pinnaPinna: A primary division of a pinnate leaf.
e; stamenStamen: The pollen-producing reproductive organ of a flower.
, at least in lowest pinnaPinna: A primary division of a pinnate leaf.
e; stamenStamen: The pollen-producing reproductive organ of a flower. filaments connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
.33. 📌Gonatopus
filaments connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
.33. 📌Gonatopus to cordateCordate:
to cordateCordate:  , sagittateSagittate:
, sagittateSagittate:  or hastateHastate:
or hastateHastate:  ; tepalTepal: A segment of the outer whorl in a flower that has no differentiation between petals and sepals.
s connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
into cup; spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
; tepalTepal: A segment of the outer whorl in a flower that has no differentiation between petals and sepals.
s connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
into cup; spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. margins connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
ly .34. 📌Stylochaeton
margins connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
ly .34. 📌Stylochaeton uniform in appearance with flowers of only one type (sometimes with sterile flowers at spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe.
uniform in appearance with flowers of only one type (sometimes with sterile flowers at spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe. base)
base) sheath with long apicalApical: Of, relating to, or denoting an apex.
liguleLigule: A narrow strap-shaped part of a plant, especially a membranous scale on the inner side of the leaf sheath at its junction with the blade.
.31. 📌Calla
sheath with long apicalApical: Of, relating to, or denoting an apex.
liguleLigule: A narrow strap-shaped part of a plant, especially a membranous scale on the inner side of the leaf sheath at its junction with the blade.
.31. 📌Calla sheath non-ligulateLigulate: Having a narrow strap-shaped part, especially a membranous scale on the inner side of the leaf sheath at its junction with the blade.
or liguleLigule: A narrow strap-shaped part of a plant, especially a membranous scale on the inner side of the leaf sheath at its junction with the blade.
only short
sheath non-ligulateLigulate: Having a narrow strap-shaped part, especially a membranous scale on the inner side of the leaf sheath at its junction with the blade.
or liguleLigule: A narrow strap-shaped part of a plant, especially a membranous scale on the inner side of the leaf sheath at its junction with the blade.
only short usually very short with non-annular insertion; trichosclereidTrichosclereid: A hard, needle-like branched cell.
s not present in tissues, leaf never perforateForate: With aperatures or openings.
d or lobed; primary lateral veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.
usually very short with non-annular insertion; trichosclereidTrichosclereid: A hard, needle-like branched cell.
s not present in tissues, leaf never perforateForate: With aperatures or openings.
d or lobed; primary lateral veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.  s forming distinct submarginal veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.
s forming distinct submarginal veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.  .8. 📌Heteropsis
.8. 📌Heteropsis well-developed with annular insertion and usually conspicuous sheath; trichosclereidTrichosclereid: A hard, needle-like branched cell.
s present in tissues, or if absent (or nearly so) then leaf with conspicuously reticulateReticulate: Reticulate Venation.
well-developed with annular insertion and usually conspicuous sheath; trichosclereidTrichosclereid: A hard, needle-like branched cell.
s present in tissues, or if absent (or nearly so) then leaf with conspicuously reticulateReticulate: Reticulate Venation. higher order venationVenation: The arrangement of veins in the leaf.
higher order venationVenation: The arrangement of veins in the leaf. and often perforateForate: With aperatures or openings.
d or lobed (Amydrium); primary lateral veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.
and often perforateForate: With aperatures or openings.
d or lobed (Amydrium); primary lateral veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.  s usually not forming distinct submarginal veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.
s usually not forming distinct submarginal veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins. 
 completely reticulateReticulate: Reticulate Venation.
completely reticulateReticulate: Reticulate Venation. ; ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals.
; ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals. 1-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
1-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary. , placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta.
, placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta. 1, intrusive-parietal, ovuleOvule: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells
1, intrusive-parietal, ovuleOvule: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells s 2 .13. 📌Amydrium
s 2 .13. 📌Amydrium parallelParallel: Parallel Venation.
parallelParallel: Parallel Venation. to primary lateral veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.
to primary lateral veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.  s, or only finest venationVenation: The arrangement of veins in the leaf.
s, or only finest venationVenation: The arrangement of veins in the leaf. reticulateReticulate: Reticulate Venation.
reticulateReticulate: Reticulate Venation.
 1-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
1-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary. or incompletely 2-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
or incompletely 2-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
 s anatropous, more than one
s anatropous, more than one s numerous, superposed on 2 (rarely 3) parietal placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta.
s numerous, superposed on 2 (rarely 3) parietal placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta. s; seeds fusiform, straight, 1.3-3.2 mm long, 0.6-1.0 mm wide.14. 📌Rhaphidophora
s; seeds fusiform, straight, 1.3-3.2 mm long, 0.6-1.0 mm wide.14. 📌Rhaphidophora s 2-4 (-6) at base of a single intrusive placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta.
s 2-4 (-6) at base of a single intrusive placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta. ; seeds curved, 3-7 mm long, 1.5-4.0 mm wide .15. 📌Epipremnum
; seeds curved, 3-7 mm long, 1.5-4.0 mm wide .15. 📌Epipremnum s amphitropous to anatropous, solitary, basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
s amphitropous to anatropous, solitary, basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
 ; neotropics (Amazonia) 18. 📌Alloschemone
; neotropics (Amazonia) 18. 📌Alloschemone 2-5 locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
2-5 locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
 s (2-)3-many per loculeLocule: A small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
s (2-)3-many per loculeLocule: A small cavity or compartment within an ovary. ; leaf blade entire
; leaf blade entire basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
; seeds fusiform to claviform; leaf blades thickly coriaceousCoriaceous: Resembling or having the texture of leather.
.20. 📌Stenospermation
basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
; seeds fusiform to claviform; leaf blades thickly coriaceousCoriaceous: Resembling or having the texture of leather.
.20. 📌Stenospermation axile; seeds lenticular and flattened, strongly curved; leaf blades mostly membranous .19. 📌Rhodospatha
axile; seeds lenticular and flattened, strongly curved; leaf blades mostly membranous .19. 📌Rhodospatha , 6-22 mm long, the raphe S-shaped; endospermEndosperm: A tissue produced inside the seeds of most of the flowering plants following fertilization. It surrounds the embryo and provides nutrition in the form of starch, though it can also contain oils and protein.
absent; ovuleOvule: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells
, 6-22 mm long, the raphe S-shaped; endospermEndosperm: A tissue produced inside the seeds of most of the flowering plants following fertilization. It surrounds the embryo and provides nutrition in the form of starch, though it can also contain oils and protein.
absent; ovuleOvule: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells s 2 per loculeLocule: A small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
s 2 per loculeLocule: A small cavity or compartment within an ovary. ; leaf blade variously shaped, often perforateForate: With aperatures or openings.
d or pinnatifidPinnatifid:
; leaf blade variously shaped, often perforateForate: With aperatures or openings.
d or pinnatifidPinnatifid:  or both .17. 📌Monstera
or both .17. 📌Monstera clearly divided into basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
female zone and apicalApical: Of, relating to, or denoting an apex.
or intermediate male zone, flowers very rarely in longitudinal rows (Spathicarpa)
clearly divided into basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
female zone and apicalApical: Of, relating to, or denoting an apex.
or intermediate male zone, flowers very rarely in longitudinal rows (Spathicarpa) fused laterally on both sides to spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
fused laterally on both sides to spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. and entirely enclosed by it, forming a septumSeptum: A partition that separates the locules of a fruit, anther, or sporangium.
dividing the spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
and entirely enclosed by it, forming a septumSeptum: A partition that separates the locules of a fruit, anther, or sporangium.
dividing the spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. into two chambers, with a single gynoecium on one side and the male flowers arranged in 2 rows on the other; very small, seasonally dormant plants endemic to western Mediterranean .87. 📌Ambrosina
into two chambers, with a single gynoecium on one side and the male flowers arranged in 2 rows on the other; very small, seasonally dormant plants endemic to western Mediterranean .87. 📌Ambrosina free or fused to spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
free or fused to spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. in various degrees but never fused laterally on both sides to spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
in various degrees but never fused laterally on both sides to spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. to form two internal chambers with a single gynoecium on one side and the male flowers on the other
to form two internal chambers with a single gynoecium on one side and the male flowers on the other s of each male flower free or only the filaments connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
s of each male flower free or only the filaments connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
 never entirely enclosed by spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
never entirely enclosed by spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. in a basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
"kettle" formed of connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
in a basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
"kettle" formed of connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. margins (if spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
margins (if spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. margins basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
ly connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
then plant never aquatic)
margins basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
ly connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
then plant never aquatic) parallel-pinnateParallel-pinnate: Parallel-Pinnate Venation.
parallel-pinnateParallel-pinnate: Parallel-Pinnate Venation.
 persisting as long as lower part; petiolePetiole: Leaf stem.
persisting as long as lower part; petiolePetiole: Leaf stem. sheath lacking liguleLigule: A narrow strap-shaped part of a plant, especially a membranous scale on the inner side of the leaf sheath at its junction with the blade.
; ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals.
sheath lacking liguleLigule: A narrow strap-shaped part of a plant, especially a membranous scale on the inner side of the leaf sheath at its junction with the blade.
; ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals. 1-many locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
1-many locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary. ; thecaeThecae: One of the lobes of an anther in which pollen is produced.
dehiscing by subapicalApical: Of, relating to, or denoting an apex.
pores or longitudinal slits; connective usually conspicuously thickened
; thecaeThecae: One of the lobes of an anther in which pollen is produced.
dehiscing by subapicalApical: Of, relating to, or denoting an apex.
pores or longitudinal slits; connective usually conspicuously thickened variously shaped, never campanulate; plants tropical American or tropical Asian; pedunclePeduncle: Flower stem.
variously shaped, never campanulate; plants tropical American or tropical Asian; pedunclePeduncle: Flower stem. usually short, if long then female flowers in single whorl (Aglaodorum)
usually short, if long then female flowers in single whorl (Aglaodorum) 1 locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
1 locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary. or incompletely 2-5 locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
or incompletely 2-5 locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary. ; most tropical Asian (except Homalomena sect. Curmeria)
; most tropical Asian (except Homalomena sect. Curmeria) 1, placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta.
1, placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta. basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
or parietal
basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
or parietal ; female flowers in spirals; stem erect to repent; placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta.
; female flowers in spirals; stem erect to repent; placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta. basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
; forest plants.72. 📌Aglaonema
basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
; forest plants.72. 📌Aglaonema ; female flowers in a single whorl; stem repent; placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta.
; female flowers in a single whorl; stem repent; placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta. parietal; on tidal mudflats.73. 📌Aglaodorum
parietal; on tidal mudflats.73. 📌Aglaodorum s several to many, placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta.
s several to many, placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta. basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
, parietal or axile
basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
, parietal or axile overtopped by flask-shaped pistillodePistillode: A sterile vestigial pistil remaining in a staminate flower.
; ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals.
overtopped by flask-shaped pistillodePistillode: A sterile vestigial pistil remaining in a staminate flower.
; ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals. 1-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
1-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary. , placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta.
, placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta. basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
.46. 📌Furtadoa
basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
.46. 📌Furtadoa s, pistillodePistillode: A sterile vestigial pistil remaining in a staminate flower.
s absent; ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals.
s, pistillodePistillode: A sterile vestigial pistil remaining in a staminate flower.
s absent; ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals. incompletely 2-5 locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
incompletely 2-5 locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary. , placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta.
, placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta. s parietal and axile .47. 📌Homalomena
s parietal and axile .47. 📌Homalomena or spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe.
or spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe. at anthesisAnthesis: The period during which pollen is presented and/or the stigma is receptive.
; endotheciumEndothecium: The lining of the cavity of an anther.
nearly always lacking cell wall thickenings; ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals.
at anthesisAnthesis: The period during which pollen is presented and/or the stigma is receptive.
; endotheciumEndothecium: The lining of the cavity of an anther.
nearly always lacking cell wall thickenings; ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals. completely 2-many locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
completely 2-many locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary. , placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta.
, placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta. axile to basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
; tropical America .45. 📌Philodendron
axile to basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
; tropical America .45. 📌Philodendron obconic to campanulate; plants from Southern Africa (naturalized in America and Asia); pedunclePeduncle: Flower stem.
obconic to campanulate; plants from Southern Africa (naturalized in America and Asia); pedunclePeduncle: Flower stem. long, sometimes longer than leaves .77. 📌Zantedeschia
long, sometimes longer than leaves .77. 📌Zantedeschia marcescentMarcescent: Withering but remaining attached to the stem.
or caducousCaducous: Easily detached and shed at an early stage.
at anthesisAnthesis: The period during which pollen is presented and/or the stigma is receptive.
, lower part long-persistentPersistent: Remaining attached to the plant beyond the usual time of falling.
; petiolePetiole: Leaf stem.
marcescentMarcescent: Withering but remaining attached to the stem.
or caducousCaducous: Easily detached and shed at an early stage.
at anthesisAnthesis: The period during which pollen is presented and/or the stigma is receptive.
, lower part long-persistentPersistent: Remaining attached to the plant beyond the usual time of falling.
; petiolePetiole: Leaf stem. sheath with long, marcescentMarcescent: Withering but remaining attached to the stem.
liguleLigule: A narrow strap-shaped part of a plant, especially a membranous scale on the inner side of the leaf sheath at its junction with the blade.
(except most Schismatoglottis spp.); ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals.
sheath with long, marcescentMarcescent: Withering but remaining attached to the stem.
liguleLigule: A narrow strap-shaped part of a plant, especially a membranous scale on the inner side of the leaf sheath at its junction with the blade.
(except most Schismatoglottis spp.); ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals. 1-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
1-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary. ; thecaeThecae: One of the lobes of an anther in which pollen is produced.
dehiscing by apicalApical: Of, relating to, or denoting an apex.
pores, connective not conspicuously thickened
; thecaeThecae: One of the lobes of an anther in which pollen is produced.
dehiscing by apicalApical: Of, relating to, or denoting an apex.
pores, connective not conspicuously thickened s parietal; thecaeThecae: One of the lobes of an anther in which pollen is produced.
truncate.
s parietal; thecaeThecae: One of the lobes of an anther in which pollen is produced.
truncate. constricted; ovuleOvule: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells
constricted; ovuleOvule: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells s anatropous to hemianatropous; petiolePetiole: Leaf stem.
s anatropous to hemianatropous; petiolePetiole: Leaf stem. sheath usually not ligulateLigulate: Having a narrow strap-shaped part, especially a membranous scale on the inner side of the leaf sheath at its junction with the blade.
; upper part of spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe.
sheath usually not ligulateLigulate: Having a narrow strap-shaped part, especially a membranous scale on the inner side of the leaf sheath at its junction with the blade.
; upper part of spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe. usually sterile .. 📌49. Schismatoglottis
usually sterile .. 📌49. Schismatoglottis not constricted; ovuleOvule: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells
not constricted; ovuleOvule: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells s hemiorthotropous to orthotropous; petiolePetiole: Leaf stem.
s hemiorthotropous to orthotropous; petiolePetiole: Leaf stem. sheath with long, marcescentMarcescent: Withering but remaining attached to the stem.
liguleLigule: A narrow strap-shaped part of a plant, especially a membranous scale on the inner side of the leaf sheath at its junction with the blade.
; spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe.
sheath with long, marcescentMarcescent: Withering but remaining attached to the stem.
liguleLigule: A narrow strap-shaped part of a plant, especially a membranous scale on the inner side of the leaf sheath at its junction with the blade.
; spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe. fertile almost to apexApex: End forming a point.
fertile almost to apexApex: End forming a point. .50. 📌Piptospatha
.50. 📌Piptospatha basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
or basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
and apicalApical: Of, relating to, or denoting an apex.
; thecaeThecae: One of the lobes of an anther in which pollen is produced.
truncate or horned
basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
or basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
and apicalApical: Of, relating to, or denoting an apex.
; thecaeThecae: One of the lobes of an anther in which pollen is produced.
truncate or horned basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
.51. 📌Hottarum
basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
.51. 📌Hottarum basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
or basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
and apicalApical: Of, relating to, or denoting an apex.
basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
or basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
and apicalApical: Of, relating to, or denoting an apex.
 smaller than ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals.
smaller than ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals. ; upper part of spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe.
; upper part of spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe. sterile with a distinct appendixAppendix: Sterile appendage at the end of a spadix.
sterile with a distinct appendixAppendix: Sterile appendage at the end of a spadix. of hornless sterile flowers; spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
of hornless sterile flowers; spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. constricted or not; stamenStamen: The pollen-producing reproductive organ of a flower.
constricted or not; stamenStamen: The pollen-producing reproductive organ of a flower. s never excavated apicalApical: Of, relating to, or denoting an apex.
ly.
s never excavated apicalApical: Of, relating to, or denoting an apex.
ly. not constricted; male flowers smooth or verrucoseVerrucose: Covered with warts or wartlike projections.
; sterile flowers between male and female flowers flattened .52. 📌Bucephalandra
not constricted; male flowers smooth or verrucoseVerrucose: Covered with warts or wartlike projections.
; sterile flowers between male and female flowers flattened .52. 📌Bucephalandra constricted; male flowers densely tuberculateTuberculate: Bearing tubercles or warty protuberances.
; sterile flowers between male and female flowers subcylindric .53. 📌Phymatarum
constricted; male flowers densely tuberculateTuberculate: Bearing tubercles or warty protuberances.
; sterile flowers between male and female flowers subcylindric .53. 📌Phymatarum as broad as ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals.
as broad as ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals. ; upper part of spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe.
; upper part of spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe. mostly fertile to apexApex: End forming a point.
mostly fertile to apexApex: End forming a point. and without a distinct appendixAppendix: Sterile appendage at the end of a spadix.
and without a distinct appendixAppendix: Sterile appendage at the end of a spadix. ; spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
; spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. not conspicuously constricted; stamenStamen: The pollen-producing reproductive organ of a flower.
not conspicuously constricted; stamenStamen: The pollen-producing reproductive organ of a flower. s all or mostly excavated apicalApical: Of, relating to, or denoting an apex.
ly
s all or mostly excavated apicalApical: Of, relating to, or denoting an apex.
ly s all excavated; placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta.
s all excavated; placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta. basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
.54. 📌Aridarum
basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
.54. 📌Aridarum s of each male flower excavated and thecaeThecae: One of the lobes of an anther in which pollen is produced.
horned, central stamenStamen: The pollen-producing reproductive organ of a flower.
s of each male flower excavated and thecaeThecae: One of the lobes of an anther in which pollen is produced.
horned, central stamenStamen: The pollen-producing reproductive organ of a flower. truncate and thecaeThecae: One of the lobes of an anther in which pollen is produced.
hornless; placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta.
truncate and thecaeThecae: One of the lobes of an anther in which pollen is produced.
hornless; placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta. s basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
(fertile ovuleOvule: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells
s basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
(fertile ovuleOvule: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells s) and apicalApical: Of, relating to, or denoting an apex.
(apparently sterile) .55. 📌Heteroaridarum
s) and apicalApical: Of, relating to, or denoting an apex.
(apparently sterile) .55. 📌Heteroaridarum reticulateReticulate: Reticulate Venation.
reticulateReticulate: Reticulate Venation.
 , leaf solitary in each growth period
, leaf solitary in each growth period usually aculeateAculeate: Sharply pointed; prickly.
; at least some of the ultimate leaf lobes trapezoidTrapezoid:
usually aculeateAculeate: Sharply pointed; prickly.
; at least some of the ultimate leaf lobes trapezoidTrapezoid:  , truncate or shallowly bifid, veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.
, truncate or shallowly bifid, veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.  s not forming regular submarginal collective veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.
s not forming regular submarginal collective veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.  on each side
on each side long; ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals.
long; ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals. 1-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
1-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary. .70. 📌Anchomanes
.70. 📌Anchomanes very short; ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals.
very short; ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals. 2-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
2-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary. .71. 📌Pseudohydrosme
.71. 📌Pseudohydrosme usually smooth, sometimes rugoseRugose: Wrinkled; corrugated.
but never aculeateAculeate: Sharply pointed; prickly.
; ultimate leaf lobes usually oblongOblong:
usually smooth, sometimes rugoseRugose: Wrinkled; corrugated.
but never aculeateAculeate: Sharply pointed; prickly.
; ultimate leaf lobes usually oblongOblong:  -ellipticElliptic:
-ellipticElliptic:  , acuminateAcuminate: Tapering to a point.
, with primary lateral veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.
, acuminateAcuminate: Tapering to a point.
, with primary lateral veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.  s forming regular submarginal collective veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.
s forming regular submarginal collective veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.  s on each side
s on each side 1-4-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
1-4-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary. ; terminal appendixAppendix: Sterile appendage at the end of a spadix.
; terminal appendixAppendix: Sterile appendage at the end of a spadix. smooth, rugoseRugose: Wrinkled; corrugated.
, rarely verrucoseVerrucose: Covered with warts or wartlike projections.
or staminodial (appendixAppendix: Sterile appendage at the end of a spadix.
smooth, rugoseRugose: Wrinkled; corrugated.
, rarely verrucoseVerrucose: Covered with warts or wartlike projections.
or staminodial (appendixAppendix: Sterile appendage at the end of a spadix. absent in Amorphophallus margaritifer and A. coudercii) .79. 📌Amorphophallus
absent in Amorphophallus margaritifer and A. coudercii) .79. 📌Amorphophallus always 1-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
always 1-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary. ; terminal appendixAppendix: Sterile appendage at the end of a spadix.
; terminal appendixAppendix: Sterile appendage at the end of a spadix. staminodial, separated from male zone by naked axial region .80. 📌Pseudodracontium
staminodial, separated from male zone by naked axial region .80. 📌Pseudodracontium ; usually several leaves present
; usually several leaves present fertile to apexApex: End forming a point.
fertile to apexApex: End forming a point. , terminal appendixAppendix: Sterile appendage at the end of a spadix.
, terminal appendixAppendix: Sterile appendage at the end of a spadix. absent
absent to hastateHastate:
to hastateHastate:  (rarely trisect) leaves; tropical America .76. 📌Montrichardia
(rarely trisect) leaves; tropical America .76. 📌Montrichardia boat-shaped, convoluteConvolute: The process of convolute vernation involves the wrapping of one margin of the leaf's blade over the other. This folding mechanism makes the emerging leaf look like a tube.
basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
ly; antherAnther: The part of a stamen that contains the pollen.
boat-shaped, convoluteConvolute: The process of convolute vernation involves the wrapping of one margin of the leaf's blade over the other. This folding mechanism makes the emerging leaf look like a tube.
basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
ly; antherAnther: The part of a stamen that contains the pollen. s lacking endothecial thickenings
s lacking endothecial thickenings 1-3-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
1-3-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary. ; spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe.
; spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe. stipitateStipitate: Having a stalk or stem.
or sessileSessile: Attached directly by its base without a stalk or peduncle.
.74. 📌Culcasia
stipitateStipitate: Having a stalk or stem.
or sessileSessile: Attached directly by its base without a stalk or peduncle.
.74. 📌Culcasia -lanceolateLanceolate:
-lanceolateLanceolate:  to cordateCordate:
to cordateCordate:  , sagittateSagittate:
, sagittateSagittate:  , hastateHastate:
, hastateHastate:  , trifidTrifid:
, trifidTrifid:  or laciniateLaciniate:
or laciniateLaciniate:  to pinnatifidPinnatifid:
to pinnatifidPinnatifid:  ; ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals.
; ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals. 1-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
1-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary. ; spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe.
; spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe. sessileSessile: Attached directly by its base without a stalk or peduncle.
.75. 📌Cercestis
sessileSessile: Attached directly by its base without a stalk or peduncle.
.75. 📌Cercestis ± fully expanded,not convoluteConvolute: The process of convolute vernation involves the wrapping of one margin of the leaf's blade over the other. This folding mechanism makes the emerging leaf look like a tube.
; antherAnther: The part of a stamen that contains the pollen.
± fully expanded,not convoluteConvolute: The process of convolute vernation involves the wrapping of one margin of the leaf's blade over the other. This folding mechanism makes the emerging leaf look like a tube.
; antherAnther: The part of a stamen that contains the pollen. s with endothecial thickenings
s with endothecial thickenings -sagittateSagittate:
-sagittateSagittate:  or subtriangular, deeply sagittateSagittate:
or subtriangular, deeply sagittateSagittate:  or trifidTrifid:
or trifidTrifid:  , glabrousGlabrous: Smooth. Free from hair or down.
; spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
, glabrousGlabrous: Smooth. Free from hair or down.
; spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. green; spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe.
green; spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe. entirely free of spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
entirely free of spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. .69. 📌Nephthytis
.69. 📌Nephthytis -ovateOvate:
-ovateOvate:  , minutely hispidHispid: Covered with stiff hair or bristles.
abaxialAbaxial: Facing away from the stem of a plant (especially denoting the lower surface of a leaf).
ly; spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
, minutely hispidHispid: Covered with stiff hair or bristles.
abaxialAbaxial: Facing away from the stem of a plant (especially denoting the lower surface of a leaf).
ly; spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. pure white; female zone of spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe.
pure white; female zone of spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe. adnateAdnate: Joined by having grown together.
to spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
adnateAdnate: Joined by having grown together.
to spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. .78. 📌Callopsis
.78. 📌Callopsis with ± smooth terminal appendixAppendix: Sterile appendage at the end of a spadix.
with ± smooth terminal appendixAppendix: Sterile appendage at the end of a spadix.
 6- to 9-ovulateOvulate: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells
6- to 9-ovulateOvulate: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells ; leaf blade trisect to pedatisect; stem a subgloboseSubglobose: Imperfectly globose ( globe-shaped ).
tuber .58. 📌Zomicarpa
; leaf blade trisect to pedatisect; stem a subgloboseSubglobose: Imperfectly globose ( globe-shaped ).
tuber .58. 📌Zomicarpa 1- to 6-ovulateOvulate: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells
1- to 6-ovulateOvulate: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells ; leaf blade cordateCordate:
; leaf blade cordateCordate:  -sagittateSagittate:
-sagittateSagittate:  ; stem a subgloboseSubglobose: Imperfectly globose ( globe-shaped ).
tuber or rhizome
; stem a subgloboseSubglobose: Imperfectly globose ( globe-shaped ).
tuber or rhizome slender
slender connective much prolonged, thread-like; stem tuberous; ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals.
connective much prolonged, thread-like; stem tuberous; ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals. 1- ovulateOvulate: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells
1- ovulateOvulate: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells .61. 📌Filarum
.61. 📌Filarum connective not at all prolonged; ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals.
connective not at all prolonged; ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals. 1-6-ovulateOvulate: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells
1-6-ovulateOvulate: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells ; stem a creeping rhizome .59. 📌Zomicarpella
; stem a creeping rhizome .59. 📌Zomicarpella relatively thick and subcylindric; stem a creeping rhizome; ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals.
relatively thick and subcylindric; stem a creeping rhizome; ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals. 1-ovulateOvulate: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells
1-ovulateOvulate: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells .60. 📌Ulearum
.60. 📌Ulearum with zone of sterile flowers between male and female zones, rarely with a naked axis between female and male zones of spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe.
with zone of sterile flowers between male and female zones, rarely with a naked axis between female and male zones of spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe. (Arum pictum) or with fertile zones contiguous (Dracunculus)
(Arum pictum) or with fertile zones contiguous (Dracunculus) parietal to subbasalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
; leaf blade sagittateSagittate:
parietal to subbasalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
; leaf blade sagittateSagittate:  or hastateHastate:
or hastateHastate:  .88. 📌Arum
.88. 📌Arum apicalApical: Of, relating to, or denoting an apex.
and/or basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
; leaf blade variously shaped
apicalApical: Of, relating to, or denoting an apex.
and/or basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
; leaf blade variously shaped s basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
and apicalApical: Of, relating to, or denoting an apex.
s basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
and apicalApical: Of, relating to, or denoting an apex.
 contiguous with female zone; leaf blade pedatifid but lobes not spirally twisted upwards .90. 📌Dracunculus
contiguous with female zone; leaf blade pedatifid but lobes not spirally twisted upwards .90. 📌Dracunculus separated from female zone by subulate to filiform sterile organs; leaf blade variously shaped
separated from female zone by subulate to filiform sterile organs; leaf blade variously shaped covered with subulate to setiform sterile flowers; leaf blade pedatifid, lobes twisting upwards on each side .91. 📌Helicodiceros
covered with subulate to setiform sterile flowers; leaf blade pedatifid, lobes twisting upwards on each side .91. 📌Helicodiceros smooth; leaf blade oblongOblong:
smooth; leaf blade oblongOblong:  -lanceolateLanceolate:
-lanceolateLanceolate:  or sagittateSagittate:
or sagittateSagittate:  -hastateHastate:
-hastateHastate:  .92. 📌Theriophonum
.92. 📌Theriophonum basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
 margins free (except Typhonium hirsutum)
margins free (except Typhonium hirsutum) relatively long, often partially naked; tropical and subtropical to warm temperate Asia to Australia .93. 📌Typhonium
relatively long, often partially naked; tropical and subtropical to warm temperate Asia to Australia .93. 📌Typhonium margins connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
for an appreciable distance (entirely free in Biarum aleppicum)
margins connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
for an appreciable distance (entirely free in Biarum aleppicum) 2-several-ovulateOvulate: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells
2-several-ovulateOvulate: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells .94. 📌Sauromatum
.94. 📌Sauromatum to ovateOvate:
to ovateOvate:  , ellipticElliptic:
, ellipticElliptic:  or obovateOvate:
or obovateOvate:  ; ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals.
; ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals. 1-ovulateOvulate: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells
1-ovulateOvulate: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells
 , spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
, spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. tube septate .95. 📌Lazarum
tube septate .95. 📌Lazarum , ovateOvate:
, ovateOvate:  , ellipticElliptic:
, ellipticElliptic:  -oblongOblong:
-oblongOblong:  or obovateOvate:
or obovateOvate:  ; spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
; spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. tube not septate .96. 📌Biarum
tube not septate .96. 📌Biarum usually without sterile flowers (sometimes present in Arisaema)
usually without sterile flowers (sometimes present in Arisaema) several-ovulateOvulate: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells
several-ovulateOvulate: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells ; female zone of spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe.
; female zone of spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe. free from spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
free from spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. ; spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
; spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. without a transverse septumSeptum: A partition that separates the locules of a fruit, anther, or sporangium.
separating male and female zones.
without a transverse septumSeptum: A partition that separates the locules of a fruit, anther, or sporangium.
separating male and female zones. margins connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
; leaf blade ovateOvate:
margins connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
; leaf blade ovateOvate:  or sagittateSagittate:
or sagittateSagittate:  .86. 📌Arisarum
.86. 📌Arisarum margins convoluteConvolute: The process of convolute vernation involves the wrapping of one margin of the leaf's blade over the other. This folding mechanism makes the emerging leaf look like a tube.
; leaf blade normally trisect, pedatisect or radiatisect, rarely simple and ovateOvate:
margins convoluteConvolute: The process of convolute vernation involves the wrapping of one margin of the leaf's blade over the other. This folding mechanism makes the emerging leaf look like a tube.
; leaf blade normally trisect, pedatisect or radiatisect, rarely simple and ovateOvate:  .98. 📌Arisaema
.98. 📌Arisaema 1-ovulateOvulate: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells
1-ovulateOvulate: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells ; female zone of spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe.
; female zone of spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe. adnateAdnate: Joined by having grown together.
to spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
adnateAdnate: Joined by having grown together.
to spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. ; spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
; spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. usually with transverse septumSeptum: A partition that separates the locules of a fruit, anther, or sporangium.
between male and female zones .97. 📌Pinellia
usually with transverse septumSeptum: A partition that separates the locules of a fruit, anther, or sporangium.
between male and female zones .97. 📌Pinellia entirely enclosed by spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
entirely enclosed by spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. in a basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
"kettle" formed of connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
in a basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
"kettle" formed of connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. margins, plants always helophyticHelophytic: A bog plant; especially a perennial marsh plant having its overwintering buds under water.
or aquatic
margins, plants always helophyticHelophytic: A bog plant; especially a perennial marsh plant having its overwintering buds under water.
or aquatic tube "kettle" with connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
margins occupying entire spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
tube "kettle" with connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
margins occupying entire spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. tube; spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
tube; spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. blade usually opening only slightly by a straight ot twisted slit; berries free, opening from base; leaf ptyxisPtyxis: The way in which an individual leaf is folded in the bud.
involuteInvolute: In involute vernation both margins on opposing sides of the leaf are rolled up forming two tubes that meet at the midrib of the leaf.
.56. 📌Lagenandra
blade usually opening only slightly by a straight ot twisted slit; berries free, opening from base; leaf ptyxisPtyxis: The way in which an individual leaf is folded in the bud.
involuteInvolute: In involute vernation both margins on opposing sides of the leaf are rolled up forming two tubes that meet at the midrib of the leaf.
.56. 📌Lagenandra tube kettle occupying only lower part of spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
tube kettle occupying only lower part of spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. tube, remainder also with connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
margins (except Cryptocoryne spiralis), blade spreading or twisted; berries connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
into a syncarp which opens from the apexApex: End forming a point.
tube, remainder also with connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
margins (except Cryptocoryne spiralis), blade spreading or twisted; berries connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
into a syncarp which opens from the apexApex: End forming a point. ; leaf ptyxisPtyxis: The way in which an individual leaf is folded in the bud.
convoluteConvolute: The process of convolute vernation involves the wrapping of one margin of the leaf's blade over the other. This folding mechanism makes the emerging leaf look like a tube.
.57. 📌Cryptocoryne
; leaf ptyxisPtyxis: The way in which an individual leaf is folded in the bud.
convoluteConvolute: The process of convolute vernation involves the wrapping of one margin of the leaf's blade over the other. This folding mechanism makes the emerging leaf look like a tube.
.57. 📌Cryptocoryne s of each male flower entirely connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
into a distinct synandriumSynandrium: Sets of stamens of which the anthers have been fused.
, synandriumSynandrium: Sets of stamens of which the anthers have been fused.
rarely reduced to single stamenStamen: The pollen-producing reproductive organ of a flower.
s of each male flower entirely connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
into a distinct synandriumSynandrium: Sets of stamens of which the anthers have been fused.
, synandriumSynandrium: Sets of stamens of which the anthers have been fused.
rarely reduced to single stamenStamen: The pollen-producing reproductive organ of a flower. (Colletogyne endemic to Madagascar) or stamenStamen: The pollen-producing reproductive organ of a flower.
(Colletogyne endemic to Madagascar) or stamenStamen: The pollen-producing reproductive organ of a flower. s free and basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
ly connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
with remote globose thecaeThecae: One of the lobes of an anther in which pollen is produced.
(Gorgonidium endemic to Andean South America), or only filaments connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
and then stigmaStigma: The receptive tip of a carpel, or of several fused carpels, in the gynoecium of a flower.
s free and basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
ly connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
with remote globose thecaeThecae: One of the lobes of an anther in which pollen is produced.
(Gorgonidium endemic to Andean South America), or only filaments connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
and then stigmaStigma: The receptive tip of a carpel, or of several fused carpels, in the gynoecium of a flower. stellate and 5-8-lobed (Spathantheum)
stellate and 5-8-lobed (Spathantheum) , each pit with a somewhat prominent upper margin; leaf peltatePeltate:
, each pit with a somewhat prominent upper margin; leaf peltatePeltate:  ; Burma to India .99. 📌Ariopsis
; Burma to India .99. 📌Ariopsis ; Africa, Madagascar or Americas
; Africa, Madagascar or Americas parallel-pinnateParallel-pinnate: Parallel-Pinnate Venation.
parallel-pinnateParallel-pinnate: Parallel-Pinnate Venation. or if reticulateReticulate: Reticulate Venation.
or if reticulateReticulate: Reticulate Venation. then stem a creeping rhizome and plant from Amazonia (Bognera)
then stem a creeping rhizome and plant from Amazonia (Bognera) s anatropous; primary lateral veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.
s anatropous; primary lateral veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.  s of leaf forming a single marginal veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.
s of leaf forming a single marginal veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.  , no submarginal collective veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.
, no submarginal collective veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.  present; plant from tropical America or continental tropical Africa.
present; plant from tropical America or continental tropical Africa. free; plant from tropical west and central Africa .48. 📌Anubias
free; plant from tropical west and central Africa .48. 📌Anubias entirely adnateAdnate: Joined by having grown together.
to spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
entirely adnateAdnate: Joined by having grown together.
to spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. ; plant from tropical America.
; plant from tropical America. strictly parallel-pinnateParallel-pinnate: Parallel-Pinnate Venation.
strictly parallel-pinnateParallel-pinnate: Parallel-Pinnate Venation. .35. 📌Dieffenbachia
.35. 📌Dieffenbachia reticulateReticulate: Reticulate Venation.
reticulateReticulate: Reticulate Venation. .36. 📌Bognera
.36. 📌Bognera s orthotropous to hemi-orthotropous; primary lateral veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.
s orthotropous to hemi-orthotropous; primary lateral veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.  s of leaf forming submarginal collective veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.
s of leaf forming submarginal collective veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.  and 1-2 marginal veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.
and 1-2 marginal veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.  s; plants from temperate eastern North America or Madagascar.
s; plants from temperate eastern North America or Madagascar. sheaths; staminodeStaminode: A sterile or abortive stamen, frequently resembling a stamen without its anther.
s of female flower free; Madagascar (also naturalized in Pemba, Zanzibar and Mascarene Is.) .85. 📌Typhonodorum
sheaths; staminodeStaminode: A sterile or abortive stamen, frequently resembling a stamen without its anther.
s of female flower free; Madagascar (also naturalized in Pemba, Zanzibar and Mascarene Is.) .85. 📌Typhonodorum reticulateReticulate: Reticulate Venation.
reticulateReticulate: Reticulate Venation. ; stem usually a subgloboseSubglobose: Imperfectly globose ( globe-shaped ).
tuber, if rhizomatous then plant Madagascan
; stem usually a subgloboseSubglobose: Imperfectly globose ( globe-shaped ).
tuber, if rhizomatous then plant Madagascan 1-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
1-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary. ; leaf venationVenation: The arrangement of veins in the leaf.
; leaf venationVenation: The arrangement of veins in the leaf. with primary lateral veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.
with primary lateral veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.  s forming submarginal collective veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.
s forming submarginal collective veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.  and 1-2 marginal veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.
and 1-2 marginal veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.  s on each side of blade
s on each side of blade s either completely connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
with marginal thecaeThecae: One of the lobes of an anther in which pollen is produced.
or only partially connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
by filaments; bisexual flowers often present between male and female zones of the spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe.
s either completely connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
with marginal thecaeThecae: One of the lobes of an anther in which pollen is produced.
or only partially connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
by filaments; bisexual flowers often present between male and female zones of the spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe. .82. 📌Carlephyton
.82. 📌Carlephyton s completely connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
into truncate synandriaSynandria: Sets of stamens of which the anthers have been fused.
or synandriaSynandria: Sets of stamens of which the anthers have been fused.
reduced to one stamenStamen: The pollen-producing reproductive organ of a flower.
s completely connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
into truncate synandriaSynandria: Sets of stamens of which the anthers have been fused.
or synandriaSynandria: Sets of stamens of which the anthers have been fused.
reduced to one stamenStamen: The pollen-producing reproductive organ of a flower.
 , thecaeThecae: One of the lobes of an anther in which pollen is produced.
apicalApical: Of, relating to, or denoting an apex.
on conical filament; spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe.
, thecaeThecae: One of the lobes of an anther in which pollen is produced.
apicalApical: Of, relating to, or denoting an apex.
on conical filament; spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe. fertile to apexApex: End forming a point.
fertile to apexApex: End forming a point. ; leaf blade always cordateCordate:
; leaf blade always cordateCordate:  .83. 📌Colletogyne
.83. 📌Colletogyne appendixAppendix: Sterile appendage at the end of a spadix.
appendixAppendix: Sterile appendage at the end of a spadix. present or not; leaf blade cordateCordate:
present or not; leaf blade cordateCordate:  , hastateHastate:
, hastateHastate:  , trifidTrifid:
, trifidTrifid:  , trisect or pedatifid .81. 📌Arophyton
, trisect or pedatifid .81. 📌Arophyton with more than 1 loculeLocule: A small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
with more than 1 loculeLocule: A small cavity or compartment within an ovary. (except Spathicarpa); leaf venationVenation: The arrangement of veins in the leaf.
(except Spathicarpa); leaf venationVenation: The arrangement of veins in the leaf. with primary lateral veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.
with primary lateral veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.  s usually forming single marginal veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.
s usually forming single marginal veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.  on each side, submarginal collective veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.
on each side, submarginal collective veinVein: Venation types: A. midrib; B. primary lateral veins; C. interprimaray veins; D. secondary veins; E. collective veins; F. tertiary veins; G. basal ribs; H. basal veins.  s usually absent
s usually absent free or only female zone adnateAdnate: Joined by having grown together.
to spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
free or only female zone adnateAdnate: Joined by having grown together.
to spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
 s anatropous
s anatropous s 2 per loculeLocule: A small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
s 2 per loculeLocule: A small cavity or compartment within an ovary. ; leaf blade entire, linearLinear:
; leaf blade entire, linearLinear:  to subsagittateSagittate:
to subsagittateSagittate:  ; spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe.
; spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe. , with terminal appendixAppendix: Sterile appendage at the end of a spadix.
, with terminal appendixAppendix: Sterile appendage at the end of a spadix. of synandrodeSynandrode: A set of fused sterile stamens.
s .37. 📌Mangonia
of synandrodeSynandrode: A set of fused sterile stamens.
s .37. 📌Mangonia s 1 per loculeLocule: A small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
s 1 per loculeLocule: A small cavity or compartment within an ovary. ; leaf blade entire, pinnatifidPinnatifid:
; leaf blade entire, pinnatifidPinnatifid:  to subdracontioidDracontioid:
to subdracontioidDracontioid:  ; spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe.
; spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe. fertile to apexApex: End forming a point.
fertile to apexApex: End forming a point.
 to bipinnatifidPinnatifid:
to bipinnatifidPinnatifid:  or subdracontioidDracontioid:
or subdracontioidDracontioid:  ; synandriaSynandria: Sets of stamens of which the anthers have been fused.
elongate; stigmaStigma: The receptive tip of a carpel, or of several fused carpels, in the gynoecium of a flower.
; synandriaSynandria: Sets of stamens of which the anthers have been fused.
elongate; stigmaStigma: The receptive tip of a carpel, or of several fused carpels, in the gynoecium of a flower. capitate or lobed; staminodeStaminode: A sterile or abortive stamen, frequently resembling a stamen without its anther.
s of female flowers free (connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
in Taccarum caudatum) .38. 📌Taccarum
capitate or lobed; staminodeStaminode: A sterile or abortive stamen, frequently resembling a stamen without its anther.
s of female flowers free (connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
in Taccarum caudatum) .38. 📌Taccarum , rarely entire; synandriaSynandria: Sets of stamens of which the anthers have been fused.
short and domed; stigmaStigma: The receptive tip of a carpel, or of several fused carpels, in the gynoecium of a flower.
, rarely entire; synandriaSynandria: Sets of stamens of which the anthers have been fused.
short and domed; stigmaStigma: The receptive tip of a carpel, or of several fused carpels, in the gynoecium of a flower. deeply lobed; staminodeStaminode: A sterile or abortive stamen, frequently resembling a stamen without its anther.
s of female flowers free or connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
.39. 📌Asterostigma
deeply lobed; staminodeStaminode: A sterile or abortive stamen, frequently resembling a stamen without its anther.
s of female flowers free or connateConnate: United so as to form a single part.
.39. 📌Asterostigma s orthotropous
s orthotropous s and synandriaSynandria: Sets of stamens of which the anthers have been fused.
elongate; leaf blade pinnatifidPinnatifid:
s and synandriaSynandria: Sets of stamens of which the anthers have been fused.
elongate; leaf blade pinnatifidPinnatifid:  or -sect or bipinnatifidPinnatifid:
or -sect or bipinnatifidPinnatifid:  or entire and ± cordateCordate:
or entire and ± cordateCordate: 
 or not; leaf blade pinnatifidPinnatifid:
or not; leaf blade pinnatifidPinnatifid:  , pinnatisectPinnatisect: Having lobes with incisions that extend almost, or up to midrib.
, pinnatisectPinnatisect: Having lobes with incisions that extend almost, or up to midrib. or bipinnatifidPinnatifid:
or bipinnatifidPinnatifid:  .40. 📌Gorgonidium
.40. 📌Gorgonidium .41. 📌Synandrospadix
.41. 📌Synandrospadix s and synandriaSynandria: Sets of stamens of which the anthers have been fused.
short and squat or synandriaSynandria: Sets of stamens of which the anthers have been fused.
very flat; staminodeStaminode: A sterile or abortive stamen, frequently resembling a stamen without its anther.
s in female flowers obovateOvate:
s and synandriaSynandria: Sets of stamens of which the anthers have been fused.
short and squat or synandriaSynandria: Sets of stamens of which the anthers have been fused.
very flat; staminodeStaminode: A sterile or abortive stamen, frequently resembling a stamen without its anther.
s in female flowers obovateOvate:  or trapezoidTrapezoid:
or trapezoidTrapezoid:  ; leaf blade pedatisect or subpalmatifid .42. 📌Gearum
; leaf blade pedatisect or subpalmatifid .42. 📌Gearum usually entirely adnateAdnate: Joined by having grown together.
to spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
usually entirely adnateAdnate: Joined by having grown together.
to spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. (male zone free in Spathantheum intermedium)
(male zone free in Spathantheum intermedium) 6-8-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
6-8-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary. ; female flowers below, male above; leaf blade entire or pinnatePinnate: Pinnate Venation.
; female flowers below, male above; leaf blade entire or pinnatePinnate: Pinnate Venation. ly lobed .43. 📌Spathantheum
ly lobed .43. 📌Spathantheum 1-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
1-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary. ; female and male flowers intermixed (2 central rows of male flowers, 2 outer rows of female flowers); leaf blade entire.44. 📌Spathicarpa
; female and male flowers intermixed (2 central rows of male flowers, 2 outer rows of female flowers); leaf blade entire.44. 📌Spathicarpa without an appendixAppendix: Sterile appendage at the end of a spadix.
without an appendixAppendix: Sterile appendage at the end of a spadix. (present in Hapaline appendiculata, included here, occasionally absent in Colocasia esculenta, excluded here)
(present in Hapaline appendiculata, included here, occasionally absent in Colocasia esculenta, excluded here) completely to incompletely 2- to several-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
completely to incompletely 2- to several-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary. with deeply intrusive parietal placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta.
with deeply intrusive parietal placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta. s (1-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
s (1-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary. with basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta.
with basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta. in Jasarum, Scaphispatha and a few species of Caladium and Xanthosoma); neotropical plants
in Jasarum, Scaphispatha and a few species of Caladium and Xanthosoma); neotropical plants , sagittateSagittate:
, sagittateSagittate:  to hastateHastate:
to hastateHastate:  or pedatifid
or pedatifid usually laterally thickened or expanded into a diaphanous mantle; leaf blade rarely peltatePeltate:
usually laterally thickened or expanded into a diaphanous mantle; leaf blade rarely peltatePeltate:  , sometimes trifidTrifid:
, sometimes trifidTrifid:  or -sect, or pedatifid or -sect
or -sect, or pedatifid or -sect tube subgloboseSubglobose: Imperfectly globose ( globe-shaped ).
, inflated; female zone of spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe.
tube subgloboseSubglobose: Imperfectly globose ( globe-shaped ).
, inflated; female zone of spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe. free; styleStyle: The usually slender part of a pistil, connecting the ovary and the stigma.
free; styleStyle: The usually slender part of a pistil, connecting the ovary and the stigma. s normally discoid (laterally swollen) and coherent (except Xanthosoma plowmanii); synandrodeSynandrode: A set of fused sterile stamens.
s (sterile flowers) between male and female flowers well-developed, ± prismatic .65. 📌Xanthosoma
s normally discoid (laterally swollen) and coherent (except Xanthosoma plowmanii); synandrodeSynandrode: A set of fused sterile stamens.
s (sterile flowers) between male and female flowers well-developed, ± prismatic .65. 📌Xanthosoma tube narrow, elongate; female zone of spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe.
tube narrow, elongate; female zone of spadixSpadix: A spike of minute flowers closely arranged around a fleshy axis and typically enclosed in a spathe. mostly adnateAdnate: Joined by having grown together.
to spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster.
mostly adnateAdnate: Joined by having grown together.
to spatheSpathe: A large sheathing bract enclosing the flower cluster. ; stylarStylar: The usually slender part of a pistil, connecting the ovary and the stigma.
; stylarStylar: The usually slender part of a pistil, connecting the ovary and the stigma. region thin, spreading, diaphanous, mantle-like; synandrodeSynandrode: A set of fused sterile stamens.
s (sterile flowers) betweeen male and female flowers usually irregular or fungiform, not prismatic .66. 📌Chlorospatha
region thin, spreading, diaphanous, mantle-like; synandrodeSynandrode: A set of fused sterile stamens.
s (sterile flowers) betweeen male and female flowers usually irregular or fungiform, not prismatic .66. 📌Chlorospatha region not laterally expanded; leaf blade usually peltatePeltate:
region not laterally expanded; leaf blade usually peltatePeltate:  , rarely trisect, never pedatifid or -sect
, rarely trisect, never pedatifid or -sect tube always convoluteConvolute: The process of convolute vernation involves the wrapping of one margin of the leaf's blade over the other. This folding mechanism makes the emerging leaf look like a tube.
; stylarStylar: The usually slender part of a pistil, connecting the ovary and the stigma.
tube always convoluteConvolute: The process of convolute vernation involves the wrapping of one margin of the leaf's blade over the other. This folding mechanism makes the emerging leaf look like a tube.
; stylarStylar: The usually slender part of a pistil, connecting the ovary and the stigma. region as broad as ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals.
region as broad as ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals. (Caladium paradoxum has discoid, coherent stylarStylar: The usually slender part of a pistil, connecting the ovary and the stigma.
(Caladium paradoxum has discoid, coherent stylarStylar: The usually slender part of a pistil, connecting the ovary and the stigma. regions); synandrodeSynandrode: A set of fused sterile stamens.
s (sterile flowers) between male and female flowers well-developed, prismatic; placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta.
regions); synandrodeSynandrode: A set of fused sterile stamens.
s (sterile flowers) between male and female flowers well-developed, prismatic; placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta. s 1-2(-3), parietal; seeds several (rarely 1-2) .63. 📌Caladium
s 1-2(-3), parietal; seeds several (rarely 1-2) .63. 📌Caladium tube gaping widely at anthesisAnthesis: The period during which pollen is presented and/or the stigma is receptive.
; styleStyle: The usually slender part of a pistil, connecting the ovary and the stigma.
tube gaping widely at anthesisAnthesis: The period during which pollen is presented and/or the stigma is receptive.
; styleStyle: The usually slender part of a pistil, connecting the ovary and the stigma. much narrower than ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals.
much narrower than ovaryOvary: The part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals. ; synandrodeSynandrode: A set of fused sterile stamens.
s (sterile flowers) lacking, male and female zones contiguous; placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta.
; synandrodeSynandrode: A set of fused sterile stamens.
s (sterile flowers) lacking, male and female zones contiguous; placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta. 1, basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
; seed solitary .62. 📌Scaphispatha
1, basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
; seed solitary .62. 📌Scaphispatha .64. 📌Jasarum
.64. 📌Jasarum clearly 1-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary.
clearly 1-locularLocular: A locule is a small cavity or compartment within an ovary. , placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta.
, placentaPlacenta: The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is referred to as the placenta. s not intrusive; palaeotropical plants
s not intrusive; palaeotropical plants s more than 1; leaf blade peltatePeltate:
s more than 1; leaf blade peltatePeltate: 
 not constricted; stem trunk-like or creeping .101. 📌Steudnera
not constricted; stem trunk-like or creeping .101. 📌Steudnera with 1 or 2 constrictions; stem tuberous, producing erect or spreading stolons bearing small tubercles covered in hooked scales .102. 📌Remusatia
with 1 or 2 constrictions; stem tuberous, producing erect or spreading stolons bearing small tubercles covered in hooked scales .102. 📌Remusatia solitary; leaf blade not peltatePeltate:
solitary; leaf blade not peltatePeltate:  .68. 📌Hapaline
.68. 📌Hapaline with an appendixAppendix: Sterile appendage at the end of a spadix.
with an appendixAppendix: Sterile appendage at the end of a spadix. (occasionally absent in Colocasia esculenta); palaeotropical plants
(occasionally absent in Colocasia esculenta); palaeotropical plants ; female flowers without staminodeStaminode: A sterile or abortive stamen, frequently resembling a stamen without its anther.
s (except single small ones in Colocasia esculenta)
; female flowers without staminodeStaminode: A sterile or abortive stamen, frequently resembling a stamen without its anther.
s (except single small ones in Colocasia esculenta) s parietal; ovuleOvule: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells
s parietal; ovuleOvule: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells s many; leaf blade always entire .103. 📌Colocasia
s many; leaf blade always entire .103. 📌Colocasia basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
; ovuleOvule: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells
basalBasal: Forming or belonging to a bottom layer or base.
; ovuleOvule: The structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells s few; leaf blade entire or pinnatifidPinnatifid:
s few; leaf blade entire or pinnatifidPinnatifid:  .104. 📌Alocasia
.104. 📌Alocasia